Type classification and characteristics of heat exchanger
Type classification and characteristics of heat exchanger
1. Definition of heat exchanger
Heat exchanger is a kind of equipment that transfers part of heat of hot fluid to cold fluid, that is to say, water or other medium is filled in a large closed container, and pipes pass through the container. Let hot water flow through the pipe.
Because of the temperature difference between the hot water in the pipeline and the cold hot water in the container, heat exchange will be formed, that is, the heat balance in junior high school physics. The heat of high-temperature objects is always transferred to low-temperature objects, so the heat of the water in the pipeline is exchanged to the cold water in the container. The heat exchanger is also called the heat exchanger.
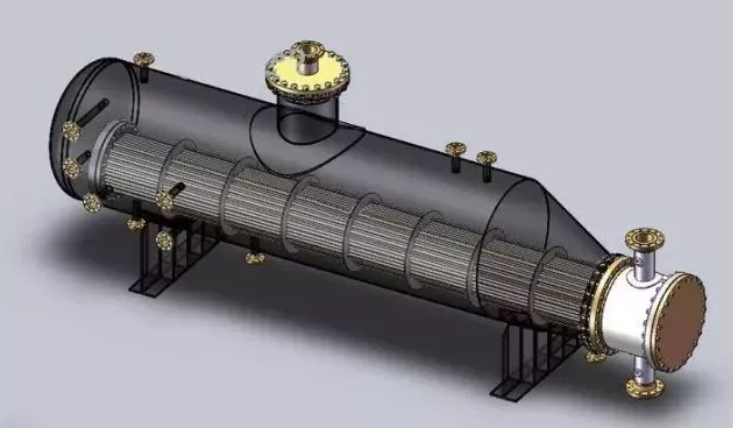
2. Classification and structure of heat exchanger
Heat exchanger can be divided into:
Cooler, condenser, heater, heat exchanger, reboiler, steam generator, waste heat (or waste heat) boiler.
According to the heat exchange mode, it can be divided into:
Direct contact heat exchanger (also called hybrid heat exchanger), regenerative heat exchanger and inter wall heat exchanger.
The following mainly introduces the heat exchanger classified by heat exchange mode:
1) direct contact heat exchanger
The direct contact heat exchanger relies on the direct contact of cold and hot fluid to conduct heat transfer. This heat transfer method avoids the fouling heat resistance of the heat transfer wall and its two sides. As long as the contact between the fluids is good, there will be a larger heat transfer rate.
Therefore, where the fluid is allowed to mix with each other, a hybrid heat exchanger can be used, such as gas washing and cooling, cooling of circulating water, mixed heating between steam and water, condensation of steam, etc. It is widely used in chemical and metallurgical enterprises, power engineering, air conditioning engineering and many other production departments.
The commonly used hybrid heat exchangers are: cooling tower, gas washing tower, jet heat exchanger and hybrid condenser.
2) regenerative heat exchanger
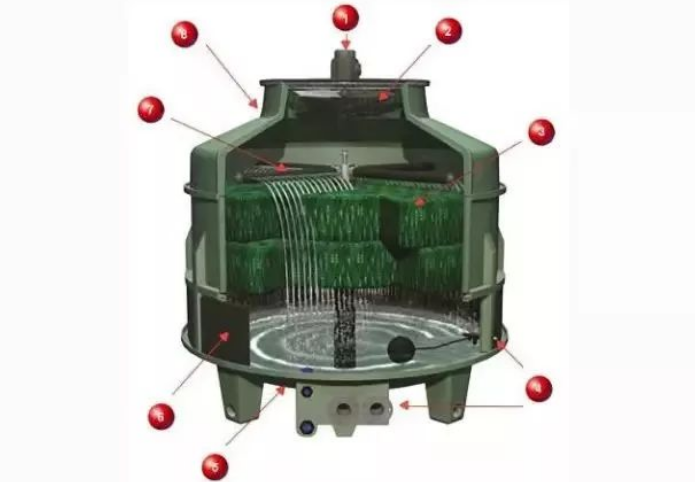

A device used for regenerative heat exchange. It is filled with solid filler to store heat.Generally, fire grids are built with refractory bricks (sometimes with metal wave belts, etc.).The heat exchange is carried out in two stages.In the first stage, the hot gas passes through the fire lattice and transmits the heat to the fire lattice for storage.In the second stage, the cold gas is heated by the heat stored in the fire lattice through the fire lattice.The two stages alternate. Generally, two regenerators are used alternately, that is, when the hot gas enters one, the cold gas enters the other. It is often used in metallurgical industry, such as regenerator of open hearth furnace.
It is also used in chemical industry, such as air preheater or combustion chamber in gas furnace and regenerative cracking furnace in artificial oil plant.
3) wall to wall heat exchanger
In this kind of heat exchanger, the cold and hot fluids are separated by a metal, so that the two fluids do not mix and carry out heat transfer.
In chemical production, the hot and cold fluid can't contact directly, so the wall heat exchanger is the most commonly used one.
The following mainly introduces the classification of wall type heat exchanger:
A) jacketed heat exchanger
It is made of vessel outer wall mounting jacket. (as shown in the figure)
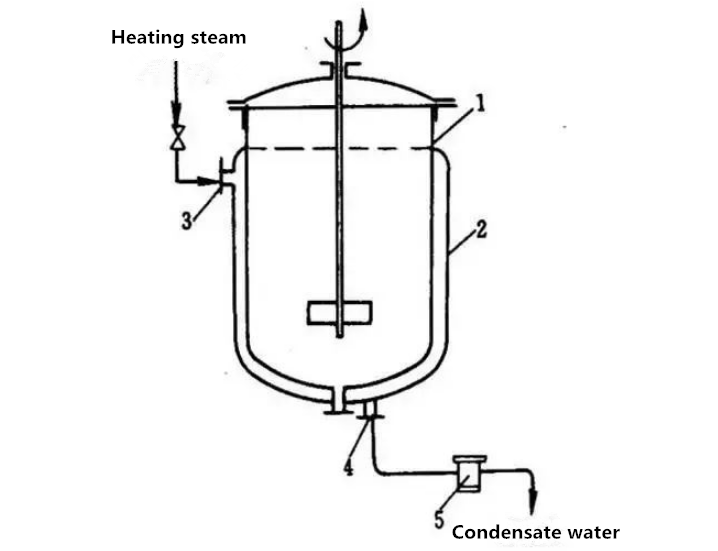
This kind of heat exchanger is made by installing a jacket on the outer wall of the container, which has a simple structure, but its heating surface is tolerant
In order to improve the heat transfer coefficient and make the liquid in the kettle heated evenly, an agitator can be installed in the kettle. When cooling water or heating agent without phase change is introduced into the jacket, a spiral diaphragm or other measures to increase turbulence can be set in the jacket to improve the heat transfer coefficient on one side of the jacket. To supplement the lack of heat transfer surface, a snake tube can also be installed in the kettle
Jacketed heat exchanger is widely used for heating and cooling of reaction process.
B) serpentine heat exchanger
Snake tube heat exchanger is divided into immersion snake tube heat exchanger and spray snake tube heat exchanger.
Immersed snake tube heat exchanger as shown in the figure
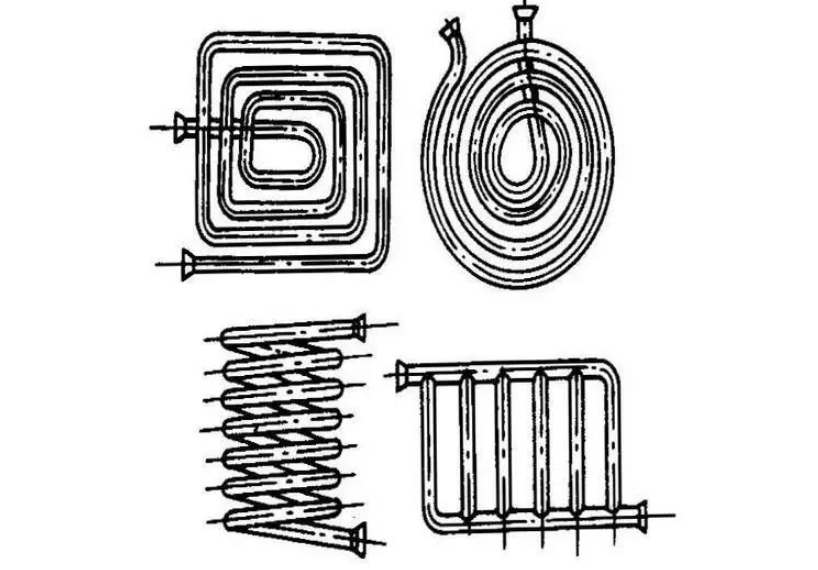
Most of the snake tubes are bent into various shapes suitable for the container with metal tubes, and immersed in the liquid in the container.
The utility model has the advantages of simple structure, can bear high pressure, and can be made of corrosion-resistant materials.
Disadvantages: the turbulence degree of the liquid in the vessel is low, and the heat transfer coefficient outside the tube is small.
Spray type snake tube heat exchanger as shown in the figure
Fix the heat exchange tubes on the steel frame in rows. The hot fluid flows in the pipe, and the cooling water evenly drips down over the device.
Advantages: the hot fluid flows in the pipe, and the cooling water evenly drips over the device. The heat transfer coefficient is large, so the heat transfer effect of spray heat exchanger is better than that of immersion snake tube heat exchanger.
However, it should be placed in the open air, occupying a large area and splashing water easily to the surrounding environment, which is inconvenient to use.
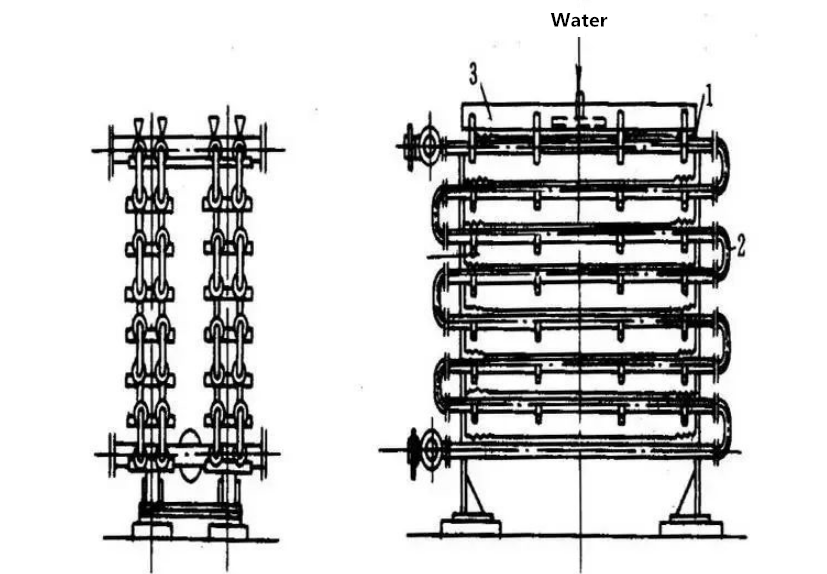
C) casing heat exchanger
As shown in the figure, the sleeve type heat exchanger is a concentric sleeve made of straight pipes with different diameters and connected by U-shaped elbows.
 Because the flow velocity of fluid inside and outside the pipe is large. Cold and hot fluid can be used as pure countercurrent, so its heat transfer coefficient is large and its heat transfer effect is good. The commonly used water tracing is a kind of simple casing heat exchanger.
Because the flow velocity of fluid inside and outside the pipe is large. Cold and hot fluid can be used as pure countercurrent, so its heat transfer coefficient is large and its heat transfer effect is good. The commonly used water tracing is a kind of simple casing heat exchanger.
D) shell and tube heat exchanger
Shell and tube heat exchanger is the most typical inter wall heat exchanger. It has a long history in industrial application, and it still occupies a leading position in all heat exchangers.
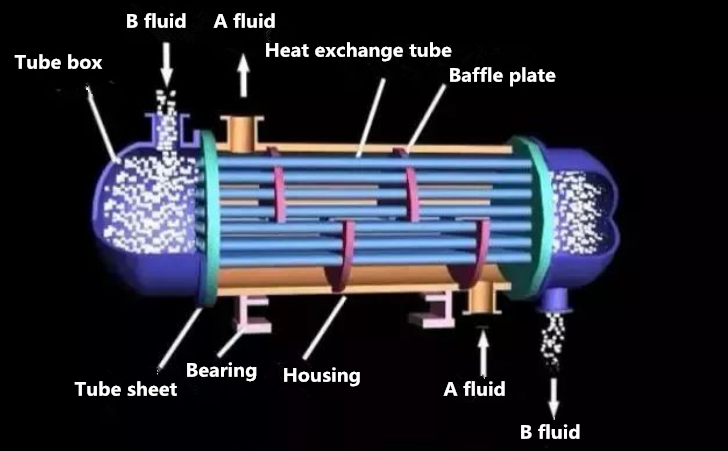
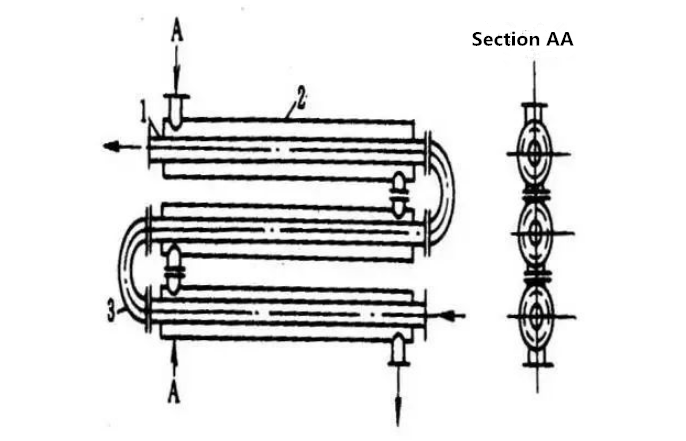
Shell and tube heat exchanger is mainly composed of shell, tube bundle, tube sheet and head. The shell is mostly round, with parallel tube bundle inside, and both ends of the tube bundle are fixed on the tube sheet.
Two kinds of fluid for heat exchange in shell and tube heat exchanger, one flows in the tube, and its stroke is called tube pass; the other flows outside the tube, and its stroke is called shell pass. The wall of the tube bundle is the heat transfer surface.
In order to improve the heat transfer coefficient of the fluid outside the tube, a certain number of transverse baffles are usually installed in the shell.
The baffle plate can not only prevent the short circuit of the fluid and increase the velocity of the fluid, but also force the fluid to cross flow through the tube bundle many times according to the specified path, which greatly increases the turbulence degree. There are two kinds of commonly used baffle plates: circular shape and circular shape (as shown in the figure below). The former is more widely used.

Every time the fluid passes through the tube bundle in the tube, it is called a tube pass, and every time it passes through the shell, it is called a shell pass. In order to improve the velocity of the fluid in the pipe, a proper partition can be set in the head at both ends to divide all the pipes into several groups.
In this way, the fluid can only pass through part of the pipe to and from the tube bundle many times at a time, which is called multi pass. Similarly, in order to improve the flow rate outside the pipe, a longitudinal baffle plate can be installed in the shell to make the fluid pass through the shell space for many times, which is called multi shell pass.
In shell and tube heat exchanger, the temperature of shell and tube bundle is different because of the difference of fluid temperature inside and outside the tube. If the temperature difference between the two is large, there will be a large thermal stress inside the heat exchanger, which may cause the tube to bend, break or loosen from the tube plate.
Therefore, when the temperature difference between tube bundle and shell exceeds 50 ℃, appropriate temperature difference compensation measures should be taken to eliminate or reduce the thermal stress.
Compensation method:
The shell is provided with expansion ring or U-tube heat exchanger and floating head heat exchanger.
Fixed tubesheet heat exchanger
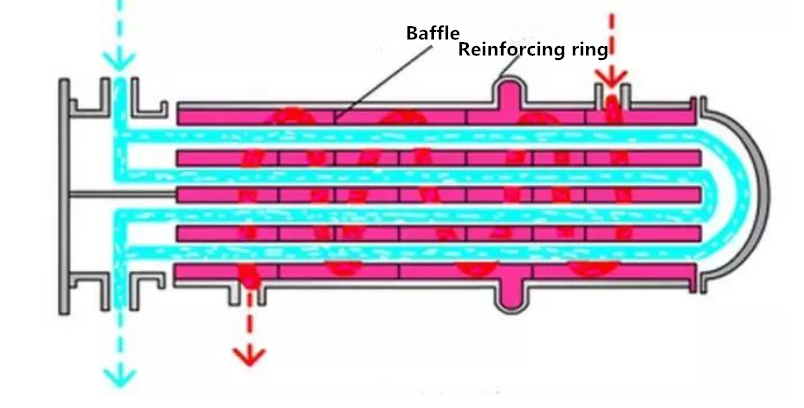
Fixed tubesheet heat exchanger can be used when the temperature difference of cold and hot flow is not large. The utility model has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, but difficult cleaning, and is not suitable for the fluid easy to scale and the fluid with large temperature difference. If the temperature difference is not large, fixed tubesheet heat exchanger with compensation ring can be used.
The figure below shows the fixed tubesheet heat exchanger with compensation ring.
Floating head heat exchanger

As shown in the figure above, one end of the tube sheet at both ends of the floating head heat exchanger can float freely along the axial direction, so as to eliminate the thermal stress. The whole tube bundle can be drawn out from the shell for easy cleaning and maintenance. But the structure is complex and the cost is high. This kind of heat exchanger is generally used in industry.
U-tube heat exchanger
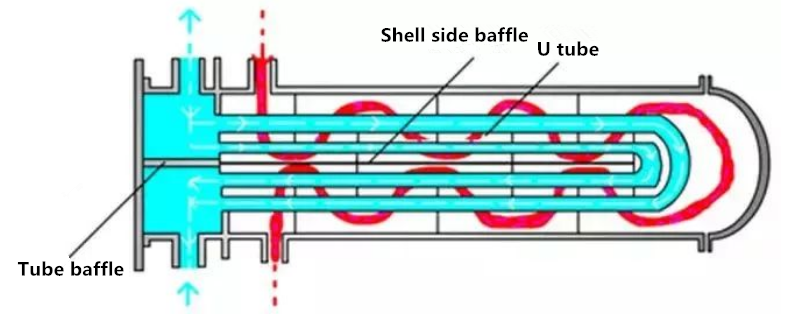
As shown in the figure above, U-tube heat exchanger, each heat exchanger tube of U-tube heat exchanger is bent into U-shape, the inlet and outlet are respectively installed on both sides of the same tube plate, and the head is divided into two chambers with partition. Each tube can be freely retracted, independent of the shell. The structure is simpler than that of floating head heat exchanger. However, the tube side is not easy to clean, so it is only suitable for clean fluid.
E) plate heat exchanger
The plate heat exchanger is composed of a set of rectangular thin metal heat transfer plates, which are clamped and assembled on the bracket by a frame.
The edge lining of two adjacent plates is compressed with gasket (made of various rubber or compressed asbestos, etc.), and the four corners of the plates have round holes to form a fluid channel.

1. Definition of heat exchanger
Heat exchanger is a kind of equipment that transfers part of heat of hot fluid to cold fluid, that is to say, water or other medium is filled in a large closed container, and pipes pass through the container. Let hot water flow through the pipe.
Because of the temperature difference between the hot water in the pipeline and the cold hot water in the container, heat exchange will be formed, that is, the heat balance in junior high school physics. The heat of high-temperature objects is always transferred to low-temperature objects, so the heat of the water in the pipeline is exchanged to the cold water in the container. The heat exchanger is also called the heat exchanger.

2. Classification and structure of heat exchanger
Heat exchanger can be divided into:
Cooler, condenser, heater, heat exchanger, reboiler, steam generator, waste heat (or waste heat) boiler.
According to the heat exchange mode, it can be divided into:
Direct contact heat exchanger (also called hybrid heat exchanger), regenerative heat exchanger and inter wall heat exchanger.
The following mainly introduces the heat exchanger classified by heat exchange mode:
1) direct contact heat exchanger
The direct contact heat exchanger relies on the direct contact of cold and hot fluid to conduct heat transfer. This heat transfer method avoids the fouling heat resistance of the heat transfer wall and its two sides. As long as the contact between the fluids is good, there will be a larger heat transfer rate.
Therefore, where the fluid is allowed to mix with each other, a hybrid heat exchanger can be used, such as gas washing and cooling, cooling of circulating water, mixed heating between steam and water, condensation of steam, etc. It is widely used in chemical and metallurgical enterprises, power engineering, air conditioning engineering and many other production departments.
The commonly used hybrid heat exchangers are: cooling tower, gas washing tower, jet heat exchanger and hybrid condenser.
2) regenerative heat exchanger

A device used for regenerative heat exchange. It is filled with solid filler to store heat.Generally, fire grids are built with refractory bricks (sometimes with metal wave belts, etc.).The heat exchange is carried out in two stages.In the first stage, the hot gas passes through the fire lattice and transmits the heat to the fire lattice for storage.In the second stage, the cold gas is heated by the heat stored in the fire lattice through the fire lattice.The two stages alternate. Generally, two regenerators are used alternately, that is, when the hot gas enters one, the cold gas enters the other. It is often used in metallurgical industry, such as regenerator of open hearth furnace.
It is also used in chemical industry, such as air preheater or combustion chamber in gas furnace and regenerative cracking furnace in artificial oil plant.
3) wall to wall heat exchanger
In this kind of heat exchanger, the cold and hot fluids are separated by a metal, so that the two fluids do not mix and carry out heat transfer.
In chemical production, the hot and cold fluid can't contact directly, so the wall heat exchanger is the most commonly used one.
The following mainly introduces the classification of wall type heat exchanger:
A) jacketed heat exchanger
It is made of vessel outer wall mounting jacket. (as shown in the figure)

This kind of heat exchanger is made by installing a jacket on the outer wall of the container, which has a simple structure, but its heating surface is tolerant
In order to improve the heat transfer coefficient and make the liquid in the kettle heated evenly, an agitator can be installed in the kettle. When cooling water or heating agent without phase change is introduced into the jacket, a spiral diaphragm or other measures to increase turbulence can be set in the jacket to improve the heat transfer coefficient on one side of the jacket. To supplement the lack of heat transfer surface, a snake tube can also be installed in the kettle
Jacketed heat exchanger is widely used for heating and cooling of reaction process.
B) serpentine heat exchanger
Snake tube heat exchanger is divided into immersion snake tube heat exchanger and spray snake tube heat exchanger.
Immersed snake tube heat exchanger as shown in the figure

Most of the snake tubes are bent into various shapes suitable for the container with metal tubes, and immersed in the liquid in the container.
The utility model has the advantages of simple structure, can bear high pressure, and can be made of corrosion-resistant materials.
Disadvantages: the turbulence degree of the liquid in the vessel is low, and the heat transfer coefficient outside the tube is small.
Spray type snake tube heat exchanger as shown in the figure

Fix the heat exchange tubes on the steel frame in rows. The hot fluid flows in the pipe, and the cooling water evenly drips down over the device.
Advantages: the hot fluid flows in the pipe, and the cooling water evenly drips over the device. The heat transfer coefficient is large, so the heat transfer effect of spray heat exchanger is better than that of immersion snake tube heat exchanger.
However, it should be placed in the open air, occupying a large area and splashing water easily to the surrounding environment, which is inconvenient to use.
C) casing heat exchanger
As shown in the figure, the sleeve type heat exchanger is a concentric sleeve made of straight pipes with different diameters and connected by U-shaped elbows.

D) shell and tube heat exchanger
Shell and tube heat exchanger is the most typical inter wall heat exchanger. It has a long history in industrial application, and it still occupies a leading position in all heat exchangers.

Tubular heat exchanger
Shell and tube heat exchanger is mainly composed of shell, tube bundle, tube sheet and head. The shell is mostly round, with parallel tube bundle inside, and both ends of the tube bundle are fixed on the tube sheet.
Two kinds of fluid for heat exchange in shell and tube heat exchanger, one flows in the tube, and its stroke is called tube pass; the other flows outside the tube, and its stroke is called shell pass. The wall of the tube bundle is the heat transfer surface.
In order to improve the heat transfer coefficient of the fluid outside the tube, a certain number of transverse baffles are usually installed in the shell.
The baffle plate can not only prevent the short circuit of the fluid and increase the velocity of the fluid, but also force the fluid to cross flow through the tube bundle many times according to the specified path, which greatly increases the turbulence degree. There are two kinds of commonly used baffle plates: circular shape and circular shape (as shown in the figure below). The former is more widely used.

Every time the fluid passes through the tube bundle in the tube, it is called a tube pass, and every time it passes through the shell, it is called a shell pass. In order to improve the velocity of the fluid in the pipe, a proper partition can be set in the head at both ends to divide all the pipes into several groups.
In this way, the fluid can only pass through part of the pipe to and from the tube bundle many times at a time, which is called multi pass. Similarly, in order to improve the flow rate outside the pipe, a longitudinal baffle plate can be installed in the shell to make the fluid pass through the shell space for many times, which is called multi shell pass.
In shell and tube heat exchanger, the temperature of shell and tube bundle is different because of the difference of fluid temperature inside and outside the tube. If the temperature difference between the two is large, there will be a large thermal stress inside the heat exchanger, which may cause the tube to bend, break or loosen from the tube plate.
Therefore, when the temperature difference between tube bundle and shell exceeds 50 ℃, appropriate temperature difference compensation measures should be taken to eliminate or reduce the thermal stress.
Compensation method:
The shell is provided with expansion ring or U-tube heat exchanger and floating head heat exchanger.
Fixed tubesheet heat exchanger
Fixed tubesheet heat exchanger can be used when the temperature difference of cold and hot flow is not large. The utility model has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, but difficult cleaning, and is not suitable for the fluid easy to scale and the fluid with large temperature difference. If the temperature difference is not large, fixed tubesheet heat exchanger with compensation ring can be used.
The figure below shows the fixed tubesheet heat exchanger with compensation ring.

Floating head heat exchanger

As shown in the figure above, one end of the tube sheet at both ends of the floating head heat exchanger can float freely along the axial direction, so as to eliminate the thermal stress. The whole tube bundle can be drawn out from the shell for easy cleaning and maintenance. But the structure is complex and the cost is high. This kind of heat exchanger is generally used in industry.
U-tube heat exchanger

As shown in the figure above, U-tube heat exchanger, each heat exchanger tube of U-tube heat exchanger is bent into U-shape, the inlet and outlet are respectively installed on both sides of the same tube plate, and the head is divided into two chambers with partition. Each tube can be freely retracted, independent of the shell. The structure is simpler than that of floating head heat exchanger. However, the tube side is not easy to clean, so it is only suitable for clean fluid.
E) plate heat exchanger
The plate heat exchanger is composed of a set of rectangular thin metal heat transfer plates, which are clamped and assembled on the bracket by a frame.
The edge lining of two adjacent plates is compressed with gasket (made of various rubber or compressed asbestos, etc.), and the four corners of the plates have round holes to form a fluid channel.





