Steel pipe production process
Production process of various steel pipes
1. seamless steel pipe production process
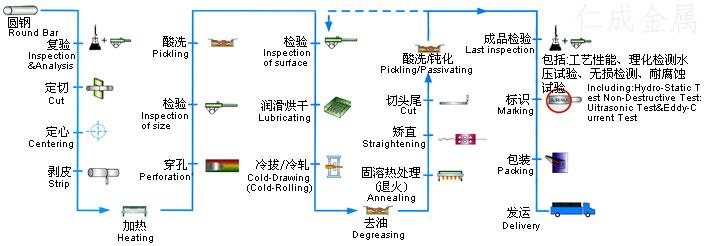
The production process of general seamless steel pipe can be divided into cold drawing and hot rolling. The production process of cold-rolled seamless steel pipe is generally more complex than hot rolling. The tube blank shall be continuously rolled with three rollers first, and then the sizing test shall be carried out after extrusion. If there is no response crack on the surface, the round tube shall be cut by the cutter, and the billet with a growth of about one meter shall be cut. Then enter the annealing process. Acid pickling shall be carried out with acid liquid for annealing. When pickling, pay attention to whether there are a lot of bubbles on the surface. If there are a lot of bubbles, it means that the quality of steel pipe can not meet the response standard. The appearance of cold-rolled seamless steel tube is shorter than that of hot-rolled seamless steel tube. The wall thickness of cold-rolled seamless steel tube is generally smaller than that of hot-rolled seamless steel tube. However, the surface of cold-rolled seamless steel tube is brighter than that of thick-walled seamless steel tube. The surface is not too rough, and the diameter is not too burr The delivery state of hot-rolled seamless steel pipe is generally after heat treatment. The hot-rolled seamless steel pipe shall be strictly selected by the staff after the quality inspection. After the quality inspection, the surface shall be coated with oil, followed by many cold drawing experiments. After the hot-rolled treatment, the perforation experiment shall be carried out. If the perforation diameter is too large, the straightening correction shall be carried out. After straightening, it is transmitted to the flaw detector by the transmission device for flaw detection test, and finally it is labeled and placed in the warehouse after specification arrangement
Hot rolled (extruded seamless steel tube)
Round tube blank → heating → piercing → three roll cross rolling, continuous rolling or extrusion → pipe detaching → sizing (or reducing) → cooling → straightening → hydrostatic test (or flaw detection) → marking → seamless steel tube in storage is made of steel ingot or solid tube blank through piercing and then hot rolling, cold rolling or cold drawing. Specification of seamless steel pipe is indicated by outer diameter * wall thickness in mm. Seamless steel pipes are divided into hot rolled and cold rolled (drawn) seamless steel pipes Hot rolled seamless steel pipe is divided into general steel pipe, low and medium pressure boiler steel pipe, high pressure boiler steel pipe, alloy steel pipe, stainless steel pipe, oil cracking pipe, geological steel pipe and other steel pipes. Cold rolled (drawn) seamless steel pipe is divided into general steel pipe, low and medium pressure boiler steel pipe, high pressure boiler steel pipe, alloy steel pipe, stainless steel pipe, petroleum cracking pipe and other steel pipes, as well as carbon thin-walled steel pipe, alloy thin-walled steel pipe, stainless thin-walled steel pipe and special-shaped steel pipe. The outer diameter of the hot-rolled seamless pipe is generally greater than 32mm, and the wall thickness is 2.5-200mm. The diameter of the cold-rolled seamless pipe can be 6mm, the wall thickness can be 0.25mm, and the outer diameter of the thin-walled pipe can be 5mm, and the wall thickness is less than 0.25mm. The size accuracy of the cold-rolled seamless pipe is higher than that of the hot-rolled seamless pipe
In general, seamless steel pipes are made of high-quality carbon Steel 16Mn, 5mnv and other low alloy structural steels such as 10, 20, 30, 35, 45 or 40Cr, 30CrMnSi, 45Mn2, 40MnB and other hot-rolled or cold-rolled ones. The seamless pipes made of 10, 20 and other low carbon steel are mainly used for fluid transmission pipes. Seamless tubes made of medium carbon steel such as 45, 40Cr are used to make mechanical parts, such as the stressed parts of automobiles and tractors. The strength and flattening test of seamless steel pipe shall be ensured. Hot rolled steel pipes shall be delivered in hot rolling or heat treatment state; cold rolled steel pipes shall be delivered in heat treatment state
Hot rolling, as the name implies, the temperature of the rolled piece is high, so the deformation resistance is small, and large deformation can be achieved. Taking the rolling of steel plate as an example, the thickness of continuous casting slab is generally about 230mm, and the final thickness is 1 ~ 20mm after rough rolling and finishing rolling. At the same time, because the width thickness ratio of steel plate is small and the requirement of dimension accuracy is relatively low, the shape problem is not easy to appear, and the control of convexity is the main way. If the structure is required, it is generally realized by controlled rolling and controlled cooling, i.e. control the start rolling temperature and final rolling temperature of finishing rolling. Round tube blank → heating → piercing → heading → annealing → pickling → oiling (copper plating) → multi pass cold drawing (cold rolling) → blank tube → heat treatment → straightening → hydrostatic test (flaw detection) → marking → warehousing
2. Production process of spiral steel pipe
Spiral steel pipe is a kind of spiral seam steel pipe, which is made of rolled strip as raw material and is often extruded and welded by automatic double wire submerged arc welding
(1) raw materials are strip coil, welding wire and flux. Before putting into operation, they must pass strict physical and chemical tests
(2) single wire or double wire submerged arc welding shall be adopted for butt joint of strip head and tail, and automatic submerged arc welding shall be adopted for repair welding after rolling steel pipe
(3) before forming, the strip steel shall be leveled, cut, planed, cleaned, transported and bent
(4) the electric contact pressure gauge is used to control the pressure of the oil cylinder on both sides of the conveyor to ensure the smooth transportation of the strip steel
(5) adopt external control or internal control roll forming
(6) weld gap control device is used to ensure that the weld gap meets the welding requirements, and the pipe diameter, misalignment and weld gap are strictly controlled
(7) both internal and external welding adopt Lincoln Electric welding machine to conduct single wire or double wire submerged arc welding, so as to obtain stable welding quality
(8) all welded joints have been inspected by on-line continuous ultrasonic automatic damage instrument, which ensures 100% coverage of non-destructive testing of spiral welds. If there is any defect, it will automatically alarm and spray the mark, and the production workers will adjust the process parameters at any time to eliminate the defect in time
(9) use air plasma cutting machine to cut the steel pipe into single pieces
(10) after cutting into single steel pipe, each batch of steel pipe shall be subject to strict first inspection system, and the mechanical properties, chemical composition, fusion condition, surface quality of steel pipe and non-destructive testing shall be inspected to ensure that the pipe manufacturing process is qualified before it is put into production
(11) the parts with continuous acoustic flaw detection marks on the weld shall be rechecked by manual ultrasonic and X-ray. If there is any defect, it shall be repaired, and then it shall be subject to NDT again until it is confirmed that the defect has been eliminated
(12) the pipe of butt weld of strip steel and T-joint intersecting with spiral weld shall be inspected by X-ray television or film
(13) each steel pipe is subject to hydrostatic test, and the pressure is sealed radially. The test pressure and time are strictly controlled by the microcomputer testing device of steel pipe water pressure. Test parameters are printed and recorded automatically
(14) the pipe end shall be machined so that the perpendicularity, slope angle and blunt edge of the end face can be accurately controlled.
3. production process of welded pipe
Welded pipe
The longitudinal welded pipe has the advantages of simple production process, high production efficiency, low cost and rapid development. The strength of spiral welded pipe is generally higher than that of straight welded pipe. It can produce welded pipe with larger diameter with narrow blank and different diameter with the same width blank. However, compared with the straight seam pipe of the same length, the weld length is increased by 30~100% and the production speed is low.
The welded pipe with large diameter or thick thickness is generally made of steel blank directly, while the thin-wall welded pipe with small welded pipe only needs to be directly welded by steel strip. Then after simple polishing, wire drawing is OK. Therefore, most of the welded pipes with smaller diameter are straight seam welded, while most of the welded pipes with large diameter are spiral welded.
4. production process of bearing steel
Bearing steel
50t UHP electric furnace smelting → 60t LF furnace refining → 60t VD furnace vacuum treatment → alloy steel rectangular billet continuous casting (260mm × 300mm, 180mm × 220mm) → slow cooling or hot delivery → rolling material → finishing → inspection and warehousing.
5. production process of galvanized pipe
(galvanized pipe)
Black parts inspection → hanging → degreasing → rinsing → pickling → cleaning → dip plating aid → hot air drying → hot dip galvanizing → internal and external blowing → cooling → passivation and rinsing → unloading → inspection and repair → typing identification → packaging, warehousing and transportation
6. forming process of straight welded pipe
Main production process description of large diameter straight seam welded pipe: large diameter straight seam welded pipe)
1. Plate probe: after the steel plate used to manufacture large-diameter submerged arc welded straight seam steel pipe enters the production line, first carry out full plate ultrasonic inspection
2. Edge milling: two sides of the steel plate are milled by the edge milling machine to achieve the required plate width, plate edge parallelism and groove shape
3. Pre bending: pre bending the plate edge with pre bending machine to make the plate edge have the required curvature
4. Forming: on the JCO molding machine, first press half of the pre bent steel plate into "J" shape after repeated step stamping, then bend the other half of the steel plate into "C" shape, and finally form the "O" shape of the opening
5. Pre welding: make the formed straight seam welded steel pipe joint and use gas shielded welding (MAG) for continuous welding
6. Internal welding: longitudinal multi wire submerged arc welding (up to four wires) is used to weld inside the straight seam steel pipe
7. External welding: longitudinal multi wire submerged arc welding is used to weld outside of LSAW steel pipe
8. Ultrasonic inspection I: conduct 100% inspection on the internal and external welds of straight welded steel pipe and the base metal on both sides of the weld
9. X-ray inspection I: 100% X-ray industrial television inspection shall be conducted for internal and external welds, and image processing system shall be adopted to ensure the sensitivity of flaw detection
10. Expanding: the full length of submerged arc welded straight seam steel pipe shall be expanded to improve the size accuracy of steel pipe and improve the distribution of internal stress of steel pipe
11. Hydrostatic test: the expanded steel pipes shall be inspected one by one on the hydrostatic test machine to ensure that the steel pipes meet the test pressure required by the standard. The machine has the function of automatic recording and storage
12. Chamfering: the qualified steel pipe shall be processed at the pipe end to meet the required pipe end groove size
13. Ultrasonic inspection II: carry out ultrasonic inspection one by one again to check the possible defects of straight seam welded steel pipe after expanding and water pressure
14. X-ray inspection II: carry out X-ray industrial television inspection and pipe end weld film for the steel pipe after expanding and hydrostatic test
15. MT for pipe end: conduct this inspection to find defects at pipe end
16. Anticorrosion and coating: the qualified steel pipe shall be anticorrosive and coated according to the user's requirements.
1. seamless steel pipe production process

The production process of general seamless steel pipe can be divided into cold drawing and hot rolling. The production process of cold-rolled seamless steel pipe is generally more complex than hot rolling. The tube blank shall be continuously rolled with three rollers first, and then the sizing test shall be carried out after extrusion. If there is no response crack on the surface, the round tube shall be cut by the cutter, and the billet with a growth of about one meter shall be cut. Then enter the annealing process. Acid pickling shall be carried out with acid liquid for annealing. When pickling, pay attention to whether there are a lot of bubbles on the surface. If there are a lot of bubbles, it means that the quality of steel pipe can not meet the response standard. The appearance of cold-rolled seamless steel tube is shorter than that of hot-rolled seamless steel tube. The wall thickness of cold-rolled seamless steel tube is generally smaller than that of hot-rolled seamless steel tube. However, the surface of cold-rolled seamless steel tube is brighter than that of thick-walled seamless steel tube. The surface is not too rough, and the diameter is not too burr The delivery state of hot-rolled seamless steel pipe is generally after heat treatment. The hot-rolled seamless steel pipe shall be strictly selected by the staff after the quality inspection. After the quality inspection, the surface shall be coated with oil, followed by many cold drawing experiments. After the hot-rolled treatment, the perforation experiment shall be carried out. If the perforation diameter is too large, the straightening correction shall be carried out. After straightening, it is transmitted to the flaw detector by the transmission device for flaw detection test, and finally it is labeled and placed in the warehouse after specification arrangement
Hot rolled (extruded seamless steel tube)
Round tube blank → heating → piercing → three roll cross rolling, continuous rolling or extrusion → pipe detaching → sizing (or reducing) → cooling → straightening → hydrostatic test (or flaw detection) → marking → seamless steel tube in storage is made of steel ingot or solid tube blank through piercing and then hot rolling, cold rolling or cold drawing. Specification of seamless steel pipe is indicated by outer diameter * wall thickness in mm. Seamless steel pipes are divided into hot rolled and cold rolled (drawn) seamless steel pipes Hot rolled seamless steel pipe is divided into general steel pipe, low and medium pressure boiler steel pipe, high pressure boiler steel pipe, alloy steel pipe, stainless steel pipe, oil cracking pipe, geological steel pipe and other steel pipes. Cold rolled (drawn) seamless steel pipe is divided into general steel pipe, low and medium pressure boiler steel pipe, high pressure boiler steel pipe, alloy steel pipe, stainless steel pipe, petroleum cracking pipe and other steel pipes, as well as carbon thin-walled steel pipe, alloy thin-walled steel pipe, stainless thin-walled steel pipe and special-shaped steel pipe. The outer diameter of the hot-rolled seamless pipe is generally greater than 32mm, and the wall thickness is 2.5-200mm. The diameter of the cold-rolled seamless pipe can be 6mm, the wall thickness can be 0.25mm, and the outer diameter of the thin-walled pipe can be 5mm, and the wall thickness is less than 0.25mm. The size accuracy of the cold-rolled seamless pipe is higher than that of the hot-rolled seamless pipe
In general, seamless steel pipes are made of high-quality carbon Steel 16Mn, 5mnv and other low alloy structural steels such as 10, 20, 30, 35, 45 or 40Cr, 30CrMnSi, 45Mn2, 40MnB and other hot-rolled or cold-rolled ones. The seamless pipes made of 10, 20 and other low carbon steel are mainly used for fluid transmission pipes. Seamless tubes made of medium carbon steel such as 45, 40Cr are used to make mechanical parts, such as the stressed parts of automobiles and tractors. The strength and flattening test of seamless steel pipe shall be ensured. Hot rolled steel pipes shall be delivered in hot rolling or heat treatment state; cold rolled steel pipes shall be delivered in heat treatment state
Hot rolling, as the name implies, the temperature of the rolled piece is high, so the deformation resistance is small, and large deformation can be achieved. Taking the rolling of steel plate as an example, the thickness of continuous casting slab is generally about 230mm, and the final thickness is 1 ~ 20mm after rough rolling and finishing rolling. At the same time, because the width thickness ratio of steel plate is small and the requirement of dimension accuracy is relatively low, the shape problem is not easy to appear, and the control of convexity is the main way. If the structure is required, it is generally realized by controlled rolling and controlled cooling, i.e. control the start rolling temperature and final rolling temperature of finishing rolling. Round tube blank → heating → piercing → heading → annealing → pickling → oiling (copper plating) → multi pass cold drawing (cold rolling) → blank tube → heat treatment → straightening → hydrostatic test (flaw detection) → marking → warehousing
2. Production process of spiral steel pipe
Spiral steel pipe is a kind of spiral seam steel pipe, which is made of rolled strip as raw material and is often extruded and welded by automatic double wire submerged arc welding
(1) raw materials are strip coil, welding wire and flux. Before putting into operation, they must pass strict physical and chemical tests
(2) single wire or double wire submerged arc welding shall be adopted for butt joint of strip head and tail, and automatic submerged arc welding shall be adopted for repair welding after rolling steel pipe
(3) before forming, the strip steel shall be leveled, cut, planed, cleaned, transported and bent
(4) the electric contact pressure gauge is used to control the pressure of the oil cylinder on both sides of the conveyor to ensure the smooth transportation of the strip steel
(5) adopt external control or internal control roll forming
(6) weld gap control device is used to ensure that the weld gap meets the welding requirements, and the pipe diameter, misalignment and weld gap are strictly controlled
(7) both internal and external welding adopt Lincoln Electric welding machine to conduct single wire or double wire submerged arc welding, so as to obtain stable welding quality
(8) all welded joints have been inspected by on-line continuous ultrasonic automatic damage instrument, which ensures 100% coverage of non-destructive testing of spiral welds. If there is any defect, it will automatically alarm and spray the mark, and the production workers will adjust the process parameters at any time to eliminate the defect in time
(9) use air plasma cutting machine to cut the steel pipe into single pieces
(10) after cutting into single steel pipe, each batch of steel pipe shall be subject to strict first inspection system, and the mechanical properties, chemical composition, fusion condition, surface quality of steel pipe and non-destructive testing shall be inspected to ensure that the pipe manufacturing process is qualified before it is put into production
(11) the parts with continuous acoustic flaw detection marks on the weld shall be rechecked by manual ultrasonic and X-ray. If there is any defect, it shall be repaired, and then it shall be subject to NDT again until it is confirmed that the defect has been eliminated
(12) the pipe of butt weld of strip steel and T-joint intersecting with spiral weld shall be inspected by X-ray television or film
(13) each steel pipe is subject to hydrostatic test, and the pressure is sealed radially. The test pressure and time are strictly controlled by the microcomputer testing device of steel pipe water pressure. Test parameters are printed and recorded automatically
(14) the pipe end shall be machined so that the perpendicularity, slope angle and blunt edge of the end face can be accurately controlled.
3. production process of welded pipe
Welded pipe
The longitudinal welded pipe has the advantages of simple production process, high production efficiency, low cost and rapid development. The strength of spiral welded pipe is generally higher than that of straight welded pipe. It can produce welded pipe with larger diameter with narrow blank and different diameter with the same width blank. However, compared with the straight seam pipe of the same length, the weld length is increased by 30~100% and the production speed is low.
The welded pipe with large diameter or thick thickness is generally made of steel blank directly, while the thin-wall welded pipe with small welded pipe only needs to be directly welded by steel strip. Then after simple polishing, wire drawing is OK. Therefore, most of the welded pipes with smaller diameter are straight seam welded, while most of the welded pipes with large diameter are spiral welded.
4. production process of bearing steel
Bearing steel
50t UHP electric furnace smelting → 60t LF furnace refining → 60t VD furnace vacuum treatment → alloy steel rectangular billet continuous casting (260mm × 300mm, 180mm × 220mm) → slow cooling or hot delivery → rolling material → finishing → inspection and warehousing.
5. production process of galvanized pipe
(galvanized pipe)
Black parts inspection → hanging → degreasing → rinsing → pickling → cleaning → dip plating aid → hot air drying → hot dip galvanizing → internal and external blowing → cooling → passivation and rinsing → unloading → inspection and repair → typing identification → packaging, warehousing and transportation
6. forming process of straight welded pipe
Main production process description of large diameter straight seam welded pipe: large diameter straight seam welded pipe)
1. Plate probe: after the steel plate used to manufacture large-diameter submerged arc welded straight seam steel pipe enters the production line, first carry out full plate ultrasonic inspection
2. Edge milling: two sides of the steel plate are milled by the edge milling machine to achieve the required plate width, plate edge parallelism and groove shape
3. Pre bending: pre bending the plate edge with pre bending machine to make the plate edge have the required curvature
4. Forming: on the JCO molding machine, first press half of the pre bent steel plate into "J" shape after repeated step stamping, then bend the other half of the steel plate into "C" shape, and finally form the "O" shape of the opening
5. Pre welding: make the formed straight seam welded steel pipe joint and use gas shielded welding (MAG) for continuous welding
6. Internal welding: longitudinal multi wire submerged arc welding (up to four wires) is used to weld inside the straight seam steel pipe
7. External welding: longitudinal multi wire submerged arc welding is used to weld outside of LSAW steel pipe
8. Ultrasonic inspection I: conduct 100% inspection on the internal and external welds of straight welded steel pipe and the base metal on both sides of the weld
9. X-ray inspection I: 100% X-ray industrial television inspection shall be conducted for internal and external welds, and image processing system shall be adopted to ensure the sensitivity of flaw detection
10. Expanding: the full length of submerged arc welded straight seam steel pipe shall be expanded to improve the size accuracy of steel pipe and improve the distribution of internal stress of steel pipe
11. Hydrostatic test: the expanded steel pipes shall be inspected one by one on the hydrostatic test machine to ensure that the steel pipes meet the test pressure required by the standard. The machine has the function of automatic recording and storage
12. Chamfering: the qualified steel pipe shall be processed at the pipe end to meet the required pipe end groove size
13. Ultrasonic inspection II: carry out ultrasonic inspection one by one again to check the possible defects of straight seam welded steel pipe after expanding and water pressure
14. X-ray inspection II: carry out X-ray industrial television inspection and pipe end weld film for the steel pipe after expanding and hydrostatic test
15. MT for pipe end: conduct this inspection to find defects at pipe end
16. Anticorrosion and coating: the qualified steel pipe shall be anticorrosive and coated according to the user's requirements.




