Selection of quenching medium
Selection of quenching medium
Quenching is the most critical process in the heat treatment process, which ultimately determines the internal quality and distortion of quenched parts. The quenching and cooling technology has been developing with the development of heat treatment technology. However, due to the complexity of the cooling process and the characteristics of instant completion, as well as the limitations of observation and measurement, the quenching cooling is somewhat mysterious.
Based on the author's experience of long-term heat treatment, this paper discusses the cognition and selection of quenching medium.
1. Basic properties of quenching medium
(1) ideal cooling speed
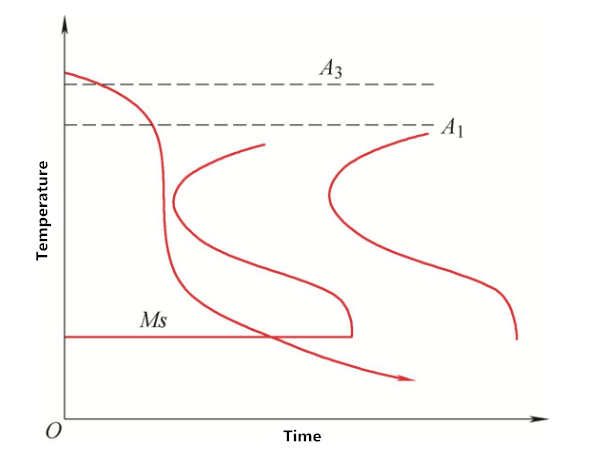
The so-called ideal cooling speed means that for a certain material and a specific quenched part, it is hoped that the cooling speed of the nose of the C curve is greater than the critical cooling speed (the minimum cooling speed to ensure that the workpiece can complete martensitic transformation). However, in other temperature ranges, especially in the martensitic transformation temperature range (MS → MF), the cooling should be slow, which is often said that "high temperature should be cooled fast, low temperature should be cooled slowly". Different steels and different workpieces have different demands for "fast" and "slow". Theoretically, there is a concept of "ideal quenching cooling medium", as shown in Figure 1. The "C" curve of different steels is different. It is impossible to obtain the so-called "ideal quenching cooling medium" suitable for quenching of various steels and workpieces of different sizes. We can only select the appropriate quenching cooling medium according to the specific situation, so as to make the quenched parts hard, with small distortion and good metallography.
(2) good stability
Quenching and cooling medium should be relatively stable in use, not easy to decompose, deteriorate and age. Many kinds of quenching oil and organic solvent exist aging phenomenon in different degrees, which should be adjusted, renewed and maintained in time.
(3) uniformity of cooling
Different parts and surfaces of the workpiece shall be cooled as evenly as possible to avoid quenching soft spots and soft blocks.
(4) non corrosive
After quenching, keep it clean, easy to clean, and do not corrode the workpiece.
(5) environmental friendly
During quenching, there is no large amount of smoke, toxic and irritant gas, and the waste liquid from quenching parts does not pollute the environment.
(6) safety
Quenching cooling medium shall not be inflammable, explosive and safe to use.
(7) economy
Quenching and cooling medium should be of both good quality and good price, which is too expensive for heat treatment enterprises to welcome.
2. Factors affecting the cooling performance of quenching medium
There are many factors that affect the cooling performance of quenching medium, which can be summarized as follows.
(1) temperature
The cooling capacity of quenching medium is different with different temperature. The cooling capacity of water and water-based quenching medium decreases with the increase of temperature, while that of oil and salt bath is the opposite. With the increase of temperature, it has good fluidity, which is conducive to heat dissipation and cooling capacity. Therefore, it is very important to grasp the cooling temperature of specific workpiece.
(2) surface tension
The surface tension directly affects the cooling speed. Generally speaking, the quenching medium with small surface tension has close contact with the surface of the quenched parts, so it has fast heat dissipation and improved cooling capacity.
(3) mixing
Stirring will increase the heat transfer coefficient of quenching medium, destroy the vapor film as early as possible, increase the cooling speed and make the quenched parts cool evenly.
(4) thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity, also known as thermal conductivity, is the physical quantity that characterizes the material's thermal conductivity. The larger the thermal conductivity is, the stronger the cooling capacity is.
(5) specific heat capacity
The larger the specific heat capacity of quenching medium is, the higher the cooling speed is.
(6) viscosity
Viscosity represents the internal friction force between liquid molecules in liquid flow. If the viscosity of quenching medium is high, its fluidity is poor, which is not conducive to convective heat dissipation, so its cooling capacity is poor. Otherwise, the cooling effect is better if the viscosity is low.
(7) heat of vaporization
Heat of vaporization refers to the heat required for a unit mass of liquid to completely change into a gas at the same temperature. The chemical stability of water is very high, and the heat capacity is large. At room temperature, it is 8 times of that of steel. The boiling point of water is low. The heat of vaporization decreases with the increase of temperature. With the increase of temperature, the cooling capacity of water drops sharply. However, when the water temperature rises to 80 ℃, the cooling capacity hardly changes, and the quenching intensity remains around 0.72.
(8) additives
The purpose of adding additives is to change the cooling performance. If a small amount of salt or alkali is added to the water, its cooling capacity will be increased several times. When polyvinyl alcohol is added into water, a very thin plastic film will be formed on the surface of the quenched part, which has poor thermal conductivity and reduces the cooling speed. The suspension or emulsion formed by oil and soap in water will accelerate the formation of steam film, increase the stability of steam film and reduce the cooling capacity. In addition, in order to change the other properties of quenching medium, people often consciously add oxidant, brightener, antirust agent, preservative and so on to affect the cooling performance to varying degrees. The addition of additives, in general, will receive the effect of more than one stroke.
(9) environment
The effect of environment on cooling capacity is often ignored. For the same temperature medium, the cooling effect is different in winter and summer, and the quenching effect is different in day and night.
3. Basic principles for selection of quenching medium
A large number of facts tell us that many quality accidents of heat treatment are related to quenching and cooling medium. If improper selection or misoperation, it will result in the waste of quenched parts. Therefore, the use of quenching medium is the basic condition to ensure product quality. No matter which quenching medium is selected, uniform quenching effect shall be obtained:
① obtain high and uniform surface hardness and enough hardening depth.
② it can not be quenched and cracked.
The quenching distortion is small. According to the specific conditions of heat treatment technical requirements, materials and shapes of quenched parts, the corresponding quench cooling medium is selected, and the following five basic principles are summarized:
(1) according to the carbon content
Carbon is the most important element in all steels. The content of carbon not only affects the properties of steels, but also the quenching effect. For carbon steel, salt water, alkali water, organic solvent, etc. shall be selected for carbon content ≤ 0.5% (mass fraction, the same below); for medium and low alloy structural steel, double liquid quenching or medium with relatively slow cooling speed shall be used; for carbon tool steel, due to high heat treatment requirements and poor hardenability, alkali bath and nitrate bath classification quenching shall be used, and oil cooling shall be rarely used.
(2) according to hardenability of steel
According to the "C" curve of steel, the steel with poor hardenability requires fast cooling speed. On the contrary, the cooling rate of steel with good hardenability is slower. According to the hardenability of steel, it is wise to choose the appropriate quenching medium.
(3) according to the effective diameter of the workpiece
Each kind of steel has a critical quenching diameter. When the surface of the quenched part is cold to MS point, the cooling speed of the medium will be greatly slowed down immediately, so will the speed of heat emission from the inside of the work piece to the quenched cooling medium. It is difficult for the supercooled austenite within a certain depth of the work piece surface to cool below MS point. When the thickness of the quenched parts is large, a faster cooling rate should be selected to obtain sufficient depth of the quenched layer. On the contrary, when the workpiece is thin, the quenching medium with low cooling rate can be used. From the maximum allowable cooling speed distribution curve, the thick workpiece can be cooled at high speed, and the thin workpiece should be cooled at low speed.
(4) according to the complexity of quenched parts
From the analysis of the distribution curve of the allowable minimum cooling speed, the quenching medium with shorter steam film stage should be selected for the workpiece with complex shape, especially for the workpiece with inner hole or deep concave surface, in order to reduce the quenching distortion and to harden the inner hole. On the contrary, if the shape of workpiece is relatively simple, quenching medium with longer vapor film stage can be used. From the maximum allowable cooling speed distribution curve, it can be seen that the cooling speed of complex workpiece is low, while that of simple workpiece is high.
(5) according to the allowable deformation
The quenched parts should have narrow cooling speed band and wide cooling speed band if the allowable distortion is large. For the allowable cooling speed bandwidth, the medium that can reach the quenching hardness generally can be used. The cooling rate zone of workpiece can be shortened by isothermal quenching or step quenching.
Due to the variety of workpiece, different requirements of heat treatment, endless quenching and cooling media, the same kind of workpiece quenching different media also get the same value of surface hardness, so it is difficult to choose quenching and cooling media. Based on the principle of economy and rationality, the relatively ideal quenching and cooling medium is selected.
4. Application example of quenching cooling medium
(1) neutral salt quenchant for high speed steel quenching
The so-called neutral salt quenchant generally refers to two formulas:
The first type: 50% bac12 + 30% KCl + 20% NaC1 (mass fraction), melting point 560 ℃, service temperature 580-620 ℃, suitable for effective diameter ≤ 20 mm, can guarantee the cooling speed ≥ 7 ℃ / s within the range of workpiece temperature 1000-800 ℃, and prevent the precipitation of eutectic carbide from affecting the performance of the tool.
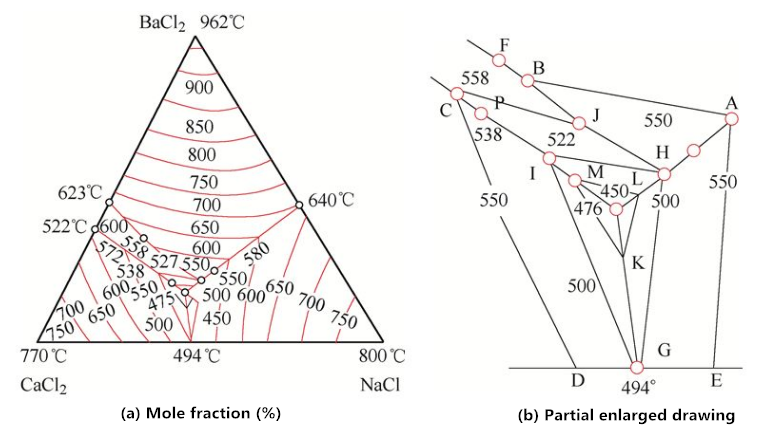
The second type: 48% CaC12 + 31% bac12 + 21% NaC1, melting point 435 ℃, service temperature 460-550 ℃. The phase diagram is shown in Figure 2. For the convenience of batching, the factory changed it to 50% CaC12 + 30% bac12 + 20% NaC1, with melting point of 440 ℃ and service temperature of 460-550 ℃. Suitable for high speed steel workpiece with effective diameter less than 40mm. The use of neutral salt of the two formulations is different. It is recommended to use CA based salt for more than 5 consecutive days in a week, because the temperature absorption of CA based salt is very strong, it is easy to deliquesce in the air; if the size of quenched parts is small and the furnace is not opened every day, it is more appropriate to use Ba based salt.
(2) salt bath quenchant
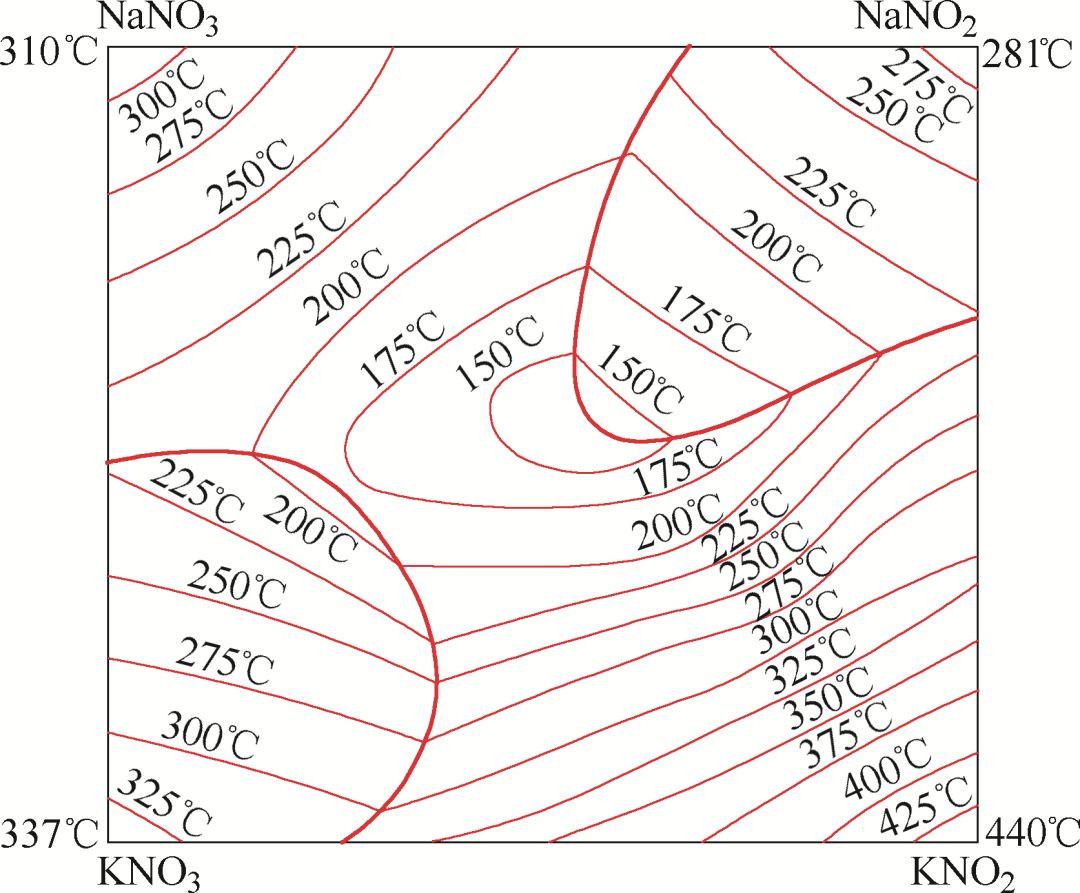
Nitrate refers to four kinds of salts: NaNO3, KNO3, NaNO2 and kno2. As a quenchant, it uses very few single components. Two or three mixed salts are commonly used. The formula and melting point are shown in Figure 3. The most commonly used formula is: 55% KNO3 + 45nano2, melting point 137 ℃, service temperature 160-550 ℃; 50% KNO3 + 50% NaNO2, melting point 140 ℃, service temperature 160-550 ℃. It is used for quenching of low alloy steel products and isothermal quenching of high speed steel and high alloy steel workpieces. Some enterprises use nitrate salt bath as the quenchant after carburizing the gear to solve the problem of heat treatment of the gear.
(3) nitrate solution quenchant
There are two nitrate water and three nitrate water.
① two nitrate water is 25% NaNO3 + 25% NaNO2 + 50% water, and the service temperature is less than 60 ℃. Due to the quenching of small tap, die and small workpiece made of 45 steel, not only the problem of quenching crack is solved, but also the quenching hardness is relatively uniform.
② trinitrate water is 25% NaNO3 + 20% NaNO2 + 20% KNO3 + 35% water. The cooling rate of trinitrate water is faster than that of water in the range of 650-550 ℃, and slower than that of water in the range of 300-200 ℃. It has been successfully used in the quenching of ductile iron, medium carbon steel, high carbon steel and low alloy steel with simple shape, and the service temperature should not exceed 60 ℃.
In practical production, carbon tool steel mould with sharp angle, groove and section size change is often encountered. The hardness requirement is 59-63hrc, water quenching is easy to crack, oil quenching is not hard, water quenching and oil cooling is difficult to ensure the quality. However, the problem is solved by isothermal quenching in nitrate water nitrate bath. That is to say, it is estimated that there is white nitrate bubble on the surface of the workpiece according to 1s / 5mm in the nitrate water. At this time, the temperature is about 200 ℃, and the workpiece is put into the 180 ℃ nitrate bath for 30-60min at once. In this way, the workpiece will not crack, has small deformation, and the hardness meets the requirements.
(4) boiling water quenching
In China, 45 steel was quenched by boiling water instead of quenching and tempering, and good results were achieved. The heating temperature of φ 40 ~ φ 80mm 45 steel was 840 ℃, and the hardness of about 250hbw was obtained by quenching in boiling water, which was very uniform. Boiling water quenching can replace normalizing treatment of 45 steel as the final heat treatment. High speed steel is quenched in boiling water at 850-870 ℃ instead of the original quenching and tempering treatment.
Bearing steel double refining treatment - boiling water quenching, because the cooling speed of boiling water is slower than that of oil, so there is no need to worry about cracking caused by boiling water quenching. The specific operation is as follows: after the final forging of bearing steel, it is immediately put into boiling water for quenching, and the workpiece is cooled to 500-400 ℃ by water and air cooling, and then (730-740 ℃) × (3-4h) annealed. After air cooling, ultrafine grains and fine carbides can be obtained.
There are many applications of boiling water quenching, not to be listed one by one, as long as the application is proper, it can save energy and increase efficiency.
(5) bluing quenchant
It is a kind of quenching and cooling medium prepared by the factory. After quenching, the workpiece is beautiful and corrosion-resistant. There are two different recipes for quenching colors. ① 70% NaNO3 + 20% KNO3 + 10% NaNO2, the workpiece is black after quenching. ② 70% NaNO2 + 20% KNO3 + 10% NaNO3, the workpiece is blue after quenching. The three kinds of nitrates are mixed evenly in proportion, and then added with appropriate amount of water to make it become supersaturated solution, and heated to 40-60 ℃ for use.
(6) water soluble polymer quenchant polyalkylene glycol (PAG)
The solubility of PAG in water decreases with the increase of temperature. The cooling rate can be adjusted by changing the concentration, temperature and stirring. PAG series coolant quenching capacity covers all fields between water and oil. PAG has been widely used in heat treatment industry since it was produced in the United States in 1960s. At present, it has successfully replaced alkali water and oil for quenching and cooling of carbon steel and low alloy steel.
(7) quenching oil
Quenching oil has been serialized, including ordinary quenching oil, bright quenching oil, fast quenching oil, fast bright quenching oil, overspeed quenching oil, vacuum quenching oil, graded quenching oil and isothermal quenching oil. Although quenching oil has many advantages as quenching and cooling medium, its disadvantages are also very prominent. For example, oil fume pollutes the environment and endangers human health. It is easy to age and cause fire. The treatment of waste oil is also a headache. In the die industry, the author suggests that the quenching oil should be eliminated as soon as possible, and the new quenching cooling medium with energy saving and environmental protection should be developed and applied.
(8) gas quenching
For the steel with high hardenability and small size, it can be gas quenched. The cooling capacity of gas is related to the type, pressure and flow rate of gas.
High speed steel mechanical blade (thickness < 20 mm) is directly air-cooled after induction heating, which can achieve high hardness of more than 63 HRC.
For Cr12 type high alloy steel, it can be quenched in air. In order to improve the cooling speed, it can be quenched by blowing. The effective size of the formwork is more than 50 mm. It can even be placed on the copper plate cooled by water.
In recent years, the development of vacuum high-pressure gas quenching is rapid. The commonly used cooling gases are N2, he, H2 and ar. H2 has the best thermal conductivity, but it is easy to explode when mixed with air, and its safety is poor. Although the cooling effect of N2 is poor, it is cheap and safe, so it is widely used.
5. summary
Choosing and using the quenching medium of heat treatment well will not only affect the product quality and economic benefit, but also endanger the survival and development of the enterprise. We should select the best quenching cooling medium according to the material and product performance requirements of the quenching workpiece of our enterprise, so as to ensure the hardening, less deformation and good performance.
Quenching is the most critical process in the heat treatment process, which ultimately determines the internal quality and distortion of quenched parts. The quenching and cooling technology has been developing with the development of heat treatment technology. However, due to the complexity of the cooling process and the characteristics of instant completion, as well as the limitations of observation and measurement, the quenching cooling is somewhat mysterious.
Based on the author's experience of long-term heat treatment, this paper discusses the cognition and selection of quenching medium.
1. Basic properties of quenching medium
(1) ideal cooling speed
The so-called ideal cooling speed means that for a certain material and a specific quenched part, it is hoped that the cooling speed of the nose of the C curve is greater than the critical cooling speed (the minimum cooling speed to ensure that the workpiece can complete martensitic transformation). However, in other temperature ranges, especially in the martensitic transformation temperature range (MS → MF), the cooling should be slow, which is often said that "high temperature should be cooled fast, low temperature should be cooled slowly". Different steels and different workpieces have different demands for "fast" and "slow". Theoretically, there is a concept of "ideal quenching cooling medium", as shown in Figure 1. The "C" curve of different steels is different. It is impossible to obtain the so-called "ideal quenching cooling medium" suitable for quenching of various steels and workpieces of different sizes. We can only select the appropriate quenching cooling medium according to the specific situation, so as to make the quenched parts hard, with small distortion and good metallography.

Figure 1 ideal quench cooling medium curve
(2) good stability
Quenching and cooling medium should be relatively stable in use, not easy to decompose, deteriorate and age. Many kinds of quenching oil and organic solvent exist aging phenomenon in different degrees, which should be adjusted, renewed and maintained in time.
(3) uniformity of cooling
Different parts and surfaces of the workpiece shall be cooled as evenly as possible to avoid quenching soft spots and soft blocks.
(4) non corrosive
After quenching, keep it clean, easy to clean, and do not corrode the workpiece.
(5) environmental friendly
During quenching, there is no large amount of smoke, toxic and irritant gas, and the waste liquid from quenching parts does not pollute the environment.
(6) safety
Quenching cooling medium shall not be inflammable, explosive and safe to use.
(7) economy
Quenching and cooling medium should be of both good quality and good price, which is too expensive for heat treatment enterprises to welcome.
2. Factors affecting the cooling performance of quenching medium
There are many factors that affect the cooling performance of quenching medium, which can be summarized as follows.
(1) temperature
The cooling capacity of quenching medium is different with different temperature. The cooling capacity of water and water-based quenching medium decreases with the increase of temperature, while that of oil and salt bath is the opposite. With the increase of temperature, it has good fluidity, which is conducive to heat dissipation and cooling capacity. Therefore, it is very important to grasp the cooling temperature of specific workpiece.
(2) surface tension
The surface tension directly affects the cooling speed. Generally speaking, the quenching medium with small surface tension has close contact with the surface of the quenched parts, so it has fast heat dissipation and improved cooling capacity.
(3) mixing
Stirring will increase the heat transfer coefficient of quenching medium, destroy the vapor film as early as possible, increase the cooling speed and make the quenched parts cool evenly.
(4) thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity, also known as thermal conductivity, is the physical quantity that characterizes the material's thermal conductivity. The larger the thermal conductivity is, the stronger the cooling capacity is.
(5) specific heat capacity
The larger the specific heat capacity of quenching medium is, the higher the cooling speed is.
(6) viscosity
Viscosity represents the internal friction force between liquid molecules in liquid flow. If the viscosity of quenching medium is high, its fluidity is poor, which is not conducive to convective heat dissipation, so its cooling capacity is poor. Otherwise, the cooling effect is better if the viscosity is low.
(7) heat of vaporization
Heat of vaporization refers to the heat required for a unit mass of liquid to completely change into a gas at the same temperature. The chemical stability of water is very high, and the heat capacity is large. At room temperature, it is 8 times of that of steel. The boiling point of water is low. The heat of vaporization decreases with the increase of temperature. With the increase of temperature, the cooling capacity of water drops sharply. However, when the water temperature rises to 80 ℃, the cooling capacity hardly changes, and the quenching intensity remains around 0.72.
(8) additives
The purpose of adding additives is to change the cooling performance. If a small amount of salt or alkali is added to the water, its cooling capacity will be increased several times. When polyvinyl alcohol is added into water, a very thin plastic film will be formed on the surface of the quenched part, which has poor thermal conductivity and reduces the cooling speed. The suspension or emulsion formed by oil and soap in water will accelerate the formation of steam film, increase the stability of steam film and reduce the cooling capacity. In addition, in order to change the other properties of quenching medium, people often consciously add oxidant, brightener, antirust agent, preservative and so on to affect the cooling performance to varying degrees. The addition of additives, in general, will receive the effect of more than one stroke.
(9) environment
The effect of environment on cooling capacity is often ignored. For the same temperature medium, the cooling effect is different in winter and summer, and the quenching effect is different in day and night.
3. Basic principles for selection of quenching medium
A large number of facts tell us that many quality accidents of heat treatment are related to quenching and cooling medium. If improper selection or misoperation, it will result in the waste of quenched parts. Therefore, the use of quenching medium is the basic condition to ensure product quality. No matter which quenching medium is selected, uniform quenching effect shall be obtained:
① obtain high and uniform surface hardness and enough hardening depth.
② it can not be quenched and cracked.
The quenching distortion is small. According to the specific conditions of heat treatment technical requirements, materials and shapes of quenched parts, the corresponding quench cooling medium is selected, and the following five basic principles are summarized:
(1) according to the carbon content
Carbon is the most important element in all steels. The content of carbon not only affects the properties of steels, but also the quenching effect. For carbon steel, salt water, alkali water, organic solvent, etc. shall be selected for carbon content ≤ 0.5% (mass fraction, the same below); for medium and low alloy structural steel, double liquid quenching or medium with relatively slow cooling speed shall be used; for carbon tool steel, due to high heat treatment requirements and poor hardenability, alkali bath and nitrate bath classification quenching shall be used, and oil cooling shall be rarely used.
(2) according to hardenability of steel
According to the "C" curve of steel, the steel with poor hardenability requires fast cooling speed. On the contrary, the cooling rate of steel with good hardenability is slower. According to the hardenability of steel, it is wise to choose the appropriate quenching medium.
(3) according to the effective diameter of the workpiece
Each kind of steel has a critical quenching diameter. When the surface of the quenched part is cold to MS point, the cooling speed of the medium will be greatly slowed down immediately, so will the speed of heat emission from the inside of the work piece to the quenched cooling medium. It is difficult for the supercooled austenite within a certain depth of the work piece surface to cool below MS point. When the thickness of the quenched parts is large, a faster cooling rate should be selected to obtain sufficient depth of the quenched layer. On the contrary, when the workpiece is thin, the quenching medium with low cooling rate can be used. From the maximum allowable cooling speed distribution curve, the thick workpiece can be cooled at high speed, and the thin workpiece should be cooled at low speed.
(4) according to the complexity of quenched parts
From the analysis of the distribution curve of the allowable minimum cooling speed, the quenching medium with shorter steam film stage should be selected for the workpiece with complex shape, especially for the workpiece with inner hole or deep concave surface, in order to reduce the quenching distortion and to harden the inner hole. On the contrary, if the shape of workpiece is relatively simple, quenching medium with longer vapor film stage can be used. From the maximum allowable cooling speed distribution curve, it can be seen that the cooling speed of complex workpiece is low, while that of simple workpiece is high.
(5) according to the allowable deformation
The quenched parts should have narrow cooling speed band and wide cooling speed band if the allowable distortion is large. For the allowable cooling speed bandwidth, the medium that can reach the quenching hardness generally can be used. The cooling rate zone of workpiece can be shortened by isothermal quenching or step quenching.
Due to the variety of workpiece, different requirements of heat treatment, endless quenching and cooling media, the same kind of workpiece quenching different media also get the same value of surface hardness, so it is difficult to choose quenching and cooling media. Based on the principle of economy and rationality, the relatively ideal quenching and cooling medium is selected.
4. Application example of quenching cooling medium
(1) neutral salt quenchant for high speed steel quenching
The so-called neutral salt quenchant generally refers to two formulas:
The first type: 50% bac12 + 30% KCl + 20% NaC1 (mass fraction), melting point 560 ℃, service temperature 580-620 ℃, suitable for effective diameter ≤ 20 mm, can guarantee the cooling speed ≥ 7 ℃ / s within the range of workpiece temperature 1000-800 ℃, and prevent the precipitation of eutectic carbide from affecting the performance of the tool.
The second type: 48% CaC12 + 31% bac12 + 21% NaC1, melting point 435 ℃, service temperature 460-550 ℃. The phase diagram is shown in Figure 2. For the convenience of batching, the factory changed it to 50% CaC12 + 30% bac12 + 20% NaC1, with melting point of 440 ℃ and service temperature of 460-550 ℃. Suitable for high speed steel workpiece with effective diameter less than 40mm. The use of neutral salt of the two formulations is different. It is recommended to use CA based salt for more than 5 consecutive days in a week, because the temperature absorption of CA based salt is very strong, it is easy to deliquesce in the air; if the size of quenched parts is small and the furnace is not opened every day, it is more appropriate to use Ba based salt.

Fig. 2 ternary phase diagram of CaC12, bac12 and NaC1
(2) salt bath quenchant
Nitrate refers to four kinds of salts: NaNO3, KNO3, NaNO2 and kno2. As a quenchant, it uses very few single components. Two or three mixed salts are commonly used. The formula and melting point are shown in Figure 3. The most commonly used formula is: 55% KNO3 + 45nano2, melting point 137 ℃, service temperature 160-550 ℃; 50% KNO3 + 50% NaNO2, melting point 140 ℃, service temperature 160-550 ℃. It is used for quenching of low alloy steel products and isothermal quenching of high speed steel and high alloy steel workpieces. Some enterprises use nitrate salt bath as the quenchant after carburizing the gear to solve the problem of heat treatment of the gear.

Fig. 3 melting curve of nitrate system
(3) nitrate solution quenchant
There are two nitrate water and three nitrate water.
① two nitrate water is 25% NaNO3 + 25% NaNO2 + 50% water, and the service temperature is less than 60 ℃. Due to the quenching of small tap, die and small workpiece made of 45 steel, not only the problem of quenching crack is solved, but also the quenching hardness is relatively uniform.
② trinitrate water is 25% NaNO3 + 20% NaNO2 + 20% KNO3 + 35% water. The cooling rate of trinitrate water is faster than that of water in the range of 650-550 ℃, and slower than that of water in the range of 300-200 ℃. It has been successfully used in the quenching of ductile iron, medium carbon steel, high carbon steel and low alloy steel with simple shape, and the service temperature should not exceed 60 ℃.
In practical production, carbon tool steel mould with sharp angle, groove and section size change is often encountered. The hardness requirement is 59-63hrc, water quenching is easy to crack, oil quenching is not hard, water quenching and oil cooling is difficult to ensure the quality. However, the problem is solved by isothermal quenching in nitrate water nitrate bath. That is to say, it is estimated that there is white nitrate bubble on the surface of the workpiece according to 1s / 5mm in the nitrate water. At this time, the temperature is about 200 ℃, and the workpiece is put into the 180 ℃ nitrate bath for 30-60min at once. In this way, the workpiece will not crack, has small deformation, and the hardness meets the requirements.
(4) boiling water quenching
In China, 45 steel was quenched by boiling water instead of quenching and tempering, and good results were achieved. The heating temperature of φ 40 ~ φ 80mm 45 steel was 840 ℃, and the hardness of about 250hbw was obtained by quenching in boiling water, which was very uniform. Boiling water quenching can replace normalizing treatment of 45 steel as the final heat treatment. High speed steel is quenched in boiling water at 850-870 ℃ instead of the original quenching and tempering treatment.
Bearing steel double refining treatment - boiling water quenching, because the cooling speed of boiling water is slower than that of oil, so there is no need to worry about cracking caused by boiling water quenching. The specific operation is as follows: after the final forging of bearing steel, it is immediately put into boiling water for quenching, and the workpiece is cooled to 500-400 ℃ by water and air cooling, and then (730-740 ℃) × (3-4h) annealed. After air cooling, ultrafine grains and fine carbides can be obtained.
There are many applications of boiling water quenching, not to be listed one by one, as long as the application is proper, it can save energy and increase efficiency.
(5) bluing quenchant
It is a kind of quenching and cooling medium prepared by the factory. After quenching, the workpiece is beautiful and corrosion-resistant. There are two different recipes for quenching colors. ① 70% NaNO3 + 20% KNO3 + 10% NaNO2, the workpiece is black after quenching. ② 70% NaNO2 + 20% KNO3 + 10% NaNO3, the workpiece is blue after quenching. The three kinds of nitrates are mixed evenly in proportion, and then added with appropriate amount of water to make it become supersaturated solution, and heated to 40-60 ℃ for use.
(6) water soluble polymer quenchant polyalkylene glycol (PAG)
The solubility of PAG in water decreases with the increase of temperature. The cooling rate can be adjusted by changing the concentration, temperature and stirring. PAG series coolant quenching capacity covers all fields between water and oil. PAG has been widely used in heat treatment industry since it was produced in the United States in 1960s. At present, it has successfully replaced alkali water and oil for quenching and cooling of carbon steel and low alloy steel.
(7) quenching oil
Quenching oil has been serialized, including ordinary quenching oil, bright quenching oil, fast quenching oil, fast bright quenching oil, overspeed quenching oil, vacuum quenching oil, graded quenching oil and isothermal quenching oil. Although quenching oil has many advantages as quenching and cooling medium, its disadvantages are also very prominent. For example, oil fume pollutes the environment and endangers human health. It is easy to age and cause fire. The treatment of waste oil is also a headache. In the die industry, the author suggests that the quenching oil should be eliminated as soon as possible, and the new quenching cooling medium with energy saving and environmental protection should be developed and applied.
(8) gas quenching
For the steel with high hardenability and small size, it can be gas quenched. The cooling capacity of gas is related to the type, pressure and flow rate of gas.
High speed steel mechanical blade (thickness < 20 mm) is directly air-cooled after induction heating, which can achieve high hardness of more than 63 HRC.
For Cr12 type high alloy steel, it can be quenched in air. In order to improve the cooling speed, it can be quenched by blowing. The effective size of the formwork is more than 50 mm. It can even be placed on the copper plate cooled by water.
In recent years, the development of vacuum high-pressure gas quenching is rapid. The commonly used cooling gases are N2, he, H2 and ar. H2 has the best thermal conductivity, but it is easy to explode when mixed with air, and its safety is poor. Although the cooling effect of N2 is poor, it is cheap and safe, so it is widely used.
5. summary
Choosing and using the quenching medium of heat treatment well will not only affect the product quality and economic benefit, but also endanger the survival and development of the enterprise. We should select the best quenching cooling medium according to the material and product performance requirements of the quenching workpiece of our enterprise, so as to ensure the hardening, less deformation and good performance.




