Hardness and tensile strength of steel pipe
Relationship between hardness and tensile strength of steel pipe
1, the relationship between hardness and tensile strength
When the hardness of steel is below 500HB, the tensile strength is proportional to the hardness, kg/mm2(óB)=1/3 X HB=3.2 X HRC=2.1 X HS, but the above relationship is not in any occasion. In the heat treatment aspect, when the tempering temperature is low, the correlation between kg/mm2 and HRC may be destroyed. The relationship between the tempering temperature, hardness and tensile strength of the steel is shown in the figure.
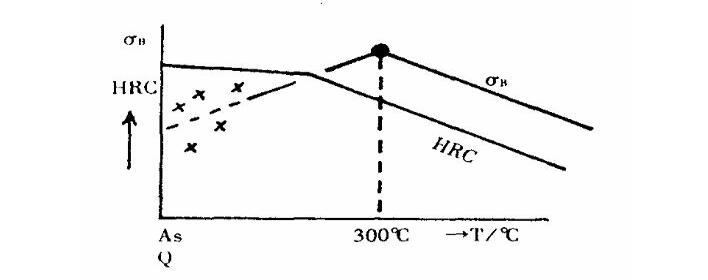
As shown in the figure, the hardness decreases with the increase of the tempering temperature, but the relationship between the hardness and the tensile strength is difficult to establish in the quenched state and the low temperature tempering below 300 °C. When the tempering temperature is around 300 °C, kg/mm2 has a correlation with HRC, that is, the hardness is high, the tensile strength is high, the hardness is low, and the tensile strength is low. It is difficult to find the value of kg/mm2 in the low temperature tempering state because the distribution of the tensile strength values is very discrete.
Since the kg/mm2 of the low-temperature tempering member is unstable and cannot be determined, it is also tested in the Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS) to measure the tensile properties of the temperature tempering member above 400 ° C (there is also a tempered workpiece at 300 ° C). In other words, the tensile test is only performed on the tempering part (quenching + 400 ° C tempering). Low temperature tempering members are used in the industry only when anti-rotation bending fatigue and wear resistance are required. Induction hardening and carburizing quenching are examples of this application. Tensile parts are not subjected to low temperature tempering. However, in low carbon steel, but quenching M can occur self-tempering (so Ms point is high), there are also users in the quenched state. The slab martensite structure of low carbon steel is self-tempered and can be applied industrially, but at this time, hardenability and mass effect must be considered (metal elements such as B, Cr, Mn should be added if necessary).
2, the hardness and tensile strength comparison table (for reference only):
2, the hardness and tensile strength comparison table (for reference only):
| Vickers hardness | Brinell hardness | Knoop hardness | Rockwell ruler | Shore hardness | Tensile Strength | ||
| HV | HB | HK | HRA | HRB | HRC | HS | Kg/m㎡ |
| 528 | 496 | 558 | 76.3 | 51 | 67.6 | 264 | |
| 513 | 481 | 542 | 75.9 | 50 | 66.2 | 255 | |
| 498 | 469 | 526 | 75.2 | 49 | 64.7 | 246 | |
| 484 | 455 | 510 | 74.7 | 48 | 63.4 | 238 | |
| 471 | 443 | 495 | 74.1 | 47 | 62.1 | 229 | |
| 458 | 432 | 480 | 73.6 | 46 | 60.8 | 221 | |
| 446 | 421 | 466 | 73.1 | 45 | 59.6 | 215 | |
| 434 | 409 | 452 | 72.5 | 44 | 58.4 | 208 | |
| 423 | 400 | 438 | 72.0 | 43 | 57.2 | 201 | |
| 412 | 390 | 426 | 71.5 | 42 | 56.1 | 194 | |
| 402 | 381 | 414 | 70.9 | 41 | 55.0 | 188 | |
| 392 | 371 | 402 | 70.4 | 40 | 53.9 | 182 | |
| 382 | 362 | 391 | 69.9 | 39 | 52.9 | 177 | |
| 372 | 353 | 380 | 69.4 | 38 | 51.8 | 171 | |
| 363 | 344 | 370 | 68.9 | 37 | 50.7 | 166 | |
| 354 | 336 | 360 | 68.4 | 36 | 49.7 | 161 | |
| 345 | 327 | 351 | 67.9 | 35 | 48.7 | 156 | |
| 336 | 319 | 342 | 67.4 | 34 | 47.7 | 152 | |
| 327 | 311 | 334 | 66.8 | 33 | 46.6 | 149 | |
| 318 | 301 | 326 | 66.3 | 32 | 45.6 | 146 | |
| 310 | 294 | 318 | 65.8 | 31 | 44.6 | 141 | |
| 302 | 286 | 311 | 65.3 | 30 | 43.6 | 138 | |
| 294 | 279 | 304 | 64.6 | 29 | 42.7 | 135 | |
| 286 | 271 | 297 | 64.3 | 28 | 41.7 | 131 | |
| 279 | 264 | 290 | 63.8 | 27 | 40.8 | 128 | |
| 272 | 258 | 284 | 63.3 | 26 | 39.9 | 125 | |
| 266 | 253 | 278 | 62.8 | 25 | 39.2 | 123 | |
| 260 | 247 | 272 | 62.4 | 24 | 38.4 | 119 | |
| 254 | 243 | 266 | 62.0 | 100 | 23 | 37.7 | 117 |
| 248 | 237 | 261 | 61.5 | 99.0 | 22 | 36.9 | 115 |
| 243 | 231 | 256 | 61.0 | 98.5 | 21 | 36.3 | 112 |
| 238 | 226 | 251 | 60.5 | 97.8 | 20 | 35.6 | 110 |
| 230 | 219 | 243 | 60.2 | 96.7 | 34.6 | 109 | |
| 222 | 212 | 236 | 59.5 | 96.3 | 33.5 | 104 | |
| 213 | 203 | 229 | 58.9 | 96.0 | 32.3 | 102 | |
| 204 | 194 | 220 | 58.3 | 95.0 | 31.1 | 100 | |
| 196 | 187 | 212 | 57.6 | 94.0 | 30.0 | 98 | |
| 188 | 179 | 204 | 57.0 | 93.0 | 94 | ||
| 180 | 171 | 196 | 56.4 | 92 | 92 | ||
| 173 | 165 | 189 | 55.8 | 91 | 90 | ||
