GB/T 8162 Seamless Steel Tubes For Structural Purposes
GB/T 8162 -2018
Seamless steel tubes for structural purposes
1 Scope
This standard specifies the order content, size, shape, weight, technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, packaging, and seamlessness of structural seamless steel tubes.
Sign and quality certificate.
This standard applies to seamless steel tubes for mechanical structures and general engineering structures.
2. Normative references
3. Ordering content
Contracts or orders for ordering steel pipes in accordance with this standard shall include the following:
a) standard number;
b) product name;
c) the grade of the steel, the quality grade should include the quality grade;
d) size specifications;
e) the quantity ordered (total weight or total length);
f) delivery status;
g) Special requirements.
4 size, shape and weight
4.1 outer diameter and wall thickness
The nominal outer diameter (D) and nominal wall thickness (S) of the steel pipe shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 1 7395. According to the requirements of the purchaser, other steel pipes of outer diameter and wall thickness can be supplied through negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
4.2 Allowable deviation of outer diameter and wall thickness
4.2.2 The allowable deviation of the outer diameter of the steel pipe shall comply with the requirements of Table 1.
4.2.2 The allowable deviation of the wall thickness of the hot milk (expanded) steel pipe shall comply with the requirements of Table 2.
4.2.3 The allowable deviation of the wall thickness of the cold drawn (milk) steel pipe shall comply with the requirements of Table 3.
4 . 2 . 4 According to the requirements of the purchaser, after consultation between the supplier and the buyer, and in the contract, the steel pipe with the allowable deviation of the dimensions specified in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 may be supplied.
4 . 3 length
4 . 3 . 1 normal length
The normal length of steel pipes is 3 000 mm to 12 000 mm. According to the requirements of the purchaser, steel pipes outside the normal length can be supplied through negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
4 . 3 . 2 range length
According to the requirements of the purchaser, after consultation between the supplier and the buyer, and in the contract, the steel pipe can be delivered according to the length of the scope.
4 . 3 . 3 length and length
4. 3. 3. 1 According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supplier and the buyer shall negotiate and indicate in the contract that the steel pipe can be delivered according to the length of the fixed length or the length of the double.
4. 3. 3. 2 When the steel pipe is delivered in fixed length or multiple length, the length tolerance shall comply with the following requirements:
a) When the length of the fixed length or the length of the double length is not more than 6 000 m, the allowable deviation is (+30,0) mm;
b) When the length of the ruler or the length of the ruler is greater than 6 000 m, the allowable deviation is (+50,0) mm.
4. 3. 3. 3 When the steel pipe is delivered in multiple lengths, the length of each double length shall be set as follows:
a) When D≤159 mm, the remaining amount of the incision is 5 mm~10 mm;
b) When D >159 mm, the remaining allowance is 10 mm~15 mm.
Steel pipes of other incisions can be supplied through negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
4 . 4 bending
4.4.1 The bending per meter of steel pipe shall comply with the requirements of Table 4.
4.4.2 The full-length bending of the steel pipe shall not exceed 0.15% of the total length of the steel pipe.
4. 5 Unroundness and uneven wall thickness
According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supplier and the buyer shall negotiate and indicate in the contract that the out-of-roundness and wall thickness of the steel pipe shall not exceed 80% of the nominal outer diameter tolerance and the nominal wall thickness tolerance respectively.
4 . 6 end shape
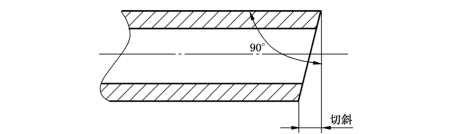
4.6.1 The steel pipe with a nominal outer diameter of not more than 60mm shall have a pipe end notching of more than 1.5 mm; for a steel pipe with a nominal outer diameter of more than 60 mm, the pipe end inclination shall not exceed 2.5% of the nominal outer diameter of the steel pipe, but the maximum shall be No more than 6 mm. The skew of the steel pipe is shown in Figure 1.
4 . 6 . 2 End cuts of steel pipes The burrs should be removed.
4 . 7 weight
4.7.1 The steel pipe is delivered according to the actual weight and can also be delivered according to the theoretical weight. The theoretical weight of the steel tube is calculated according to the provisions of GB/T 17395, and the density of the steel is 7.85 kg/dm3.
4 . 7 . 2 According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supplier and the buyer shall negotiate and indicate in the contract that the deviation between the theoretical weight of the delivered steel pipe and the actual weight shall comply with the following provisions:
a) Single steel pipe: ±10%;
b) Steel pipes with a minimum of 10 t per batch: ± 7.5 %.
5 Technical requirements
5. 1 Steel grade and chemical composition
5.1.1 The grade and chemical composition of the high-quality carbon structural steel (melting analysis) shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 699.
5.1.2 The grade and chemical composition of the low-alloy high-strength structural steel (melting analysis) shall comply with the requirements of Table 5. Except for quality class A, the carbon equivalent of each grade shall comply with the requirements of Table 6. The carbon equivalent (CEV) should be calculated from the smelting analysis component according to formula (1).
CEV = C + Mn/6 + (Cr + Mo + V) /5 + (Ni + Cu) /15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .(1)
5.1.3 Alloy structural steel grades and chemical composition (melting analysis) shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 3077.
5. 1. 4 According to the requirements of the purchaser, steel pipes of other grades or chemical compositions may be supplied through negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
5 . 1 . 5 When the purchaser requests to perform a finished product analysis, it should be indicated in the contract. The allowable deviation of the chemical composition of the finished steel pipe shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 222.
5 . 2 Manufacturing methods
5 . 2 . 1 steel smelting method
Steel should be smelted by electric arc furnace plus furnace refining or oxygen converter plus furnace refining method. After consultation between the supply and demand sides, other methods of higher requirements may also be used for smelting. When the purchaser specifies a certain smelting method, it should be indicated in the contract.
Manufacturing Method 5. 2.2 shell of
5. 2. 2. 1 Tube blanks can be manufactured by continuous casting, die casting or hot milk (forging).
5. 2. 2. 2 continuous casting tube blanks shall comply with the provisions of YB/T 4149; hot milk (forged) tube blanks shall comply with the provisions of YB/T 5221 or YB/T 5222; the molded tube blanks may refer to hot milk ( The implementation of the forging) tube blank.
5 . 2 . 3 manufacturing method of steel pipe
Steel pipes shall be manufactured by hot milk (expansion) or cold drawing (milk) without seaming. When the purchaser specifies a method to manufacture steel pipes, it should be indicated in the contract.
5 . 3 delivery status
5.3.1 Hot milk (expanded) steel pipes are delivered in hot milk (expanded) or heat treated condition. When the purchaser requests the heat treatment status, it shall be indicated in the contract.
5 . 3 . 2 Cold drawn (milk) steel pipes shall be delivered in an annealed or high temperature tempered condition. According to the requirements of the purchaser, after consultation between the supplier and the buyer, and in the contract, the cold drawn (milk) steel pipe can also be delivered in cold drawn (milk) or other heat treatment conditions.
5.4 Mechanical properties
5 . 4 . 1 tensile properties
5.4.1.1 For steel pipes of high quality carbon structural steel and low alloy high strength structural steel, the tensile properties in the delivery state shall comply with the requirements of Table 7.
5. 4. 1. 2 alloy structural steel pipe specimen blanks According to the recommended heat treatment system in Table 8, the tensile properties measured after the heat treatment is prepared shall comply with the requirements of Table 8.
5. 4. 1. 3 Cold drawing (milk) state The mechanical properties of the delivered steel pipe shall be determined by negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
GB/T 8162—2018
5 . 4. 2 hardness
Alloy structure steel pipes with annealed or high temperature tempered condition and wall thickness not less than 5 m m shall have a Brinell hardness as specified in Table 8.
5.4.3 Impact
5. 4. 3. 1 Low-alloy high-strength structural steel pipe, when the outer diameter is not less than 70 mm and the wall thickness is not less than 6.5 mm, the longitudinal impact test shall be carried out, and the test temperature of the Charpy V-notch impact test and The energy absorbed by the impact shall comply with the requirements of Table 7. The shock absorption energy is calculated as the arithmetic mean of a set of 3 samples, allowing a single value of one of the samples to be lower than the specified value, but not less than 70% of the specified value.
5. 4. 3. 2 The impact absorption energy in Table 7 is the Charpy V-notch impact absorption energy requirement value of the standard size sample. When the size of the steel pipe cannot prepare a standard size sample, a small size sample can be prepared. When using small-sized impact specimens, the minimum Charpy V-notch impact energy requirements should be the standard-size specimen impact energy requirements multiplied by the decreasing factor in Table 9. The size of the impact specimen should be preferentially selected to a larger size.
5. 4. 3. 3 According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supplier and the buyer shall negotiate and indicate in the contract that the other grades of the steel pipe may also be subjected to the Charpy V-notch impact test. The test temperature, test size and impact absorption energy are The supply and demand sides will negotiate and determine.
5 . 5 process performance
5 . 5 . 1 flattening
The grades are 10, 15, 20, 25, 20Mn, 25Mn, Q345, Q390, the nominal outer diameter is >22 mm~600mm, and the steel pipe with the wall thickness to outer diameter ratio of not more than 10% shall be crushed and tested. The distance between the plates should meet the requirements of Table 10. After crushing, on the sample
There should be no cracks or cracks.
Table 10 Distance between flat steel plates
5.5.2 Bending
According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supply and demand sides negotiate and indicate in the contract that the steel pipe with an outer diameter of not more than 22mm can be bent. The bending angle is 90°, and the radius of the core is 6 times the outer diameter of the steel pipe. There should be no cracks or cracks in the bend.
5 . 6 surface quality
The inner and outer surfaces of the steel pipe should not have visible cracks, folds, crusting, milk breaks and separation. These defects shall be completely removed and the depth of removal shall not exceed the lower deviation of the nominal wall thickness. The actual wall thickness at the cleaning site shall not be less than the minimum allowed by the wall thickness. Other local imperfections that do not exceed the deviation below the wall thickness are allowed to exist.
5 . 7 Nondestructive testing
According to the requirements of the purchaser, after consultation between the supplier and the buyer, and in the contract, the steel pipe can be non-destructively tested by one or more of the following methods:
A) The ultrasonic testing predetermined GB / T 5777-2008, and comparison sample tube groove depth levels: cold drawing (rolled) pipe for L3, rolled (expanded) steel pipe L4;
b) eddy current inspection according to the provisions of GB/T 7735—201 6 , acceptance level E4H or E4;
c) Magnetic flux leakage test according to GB/T 12606—201 6 and acceptance level F4.
5 . 8 galvanized layer
According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supply and demand sides negotiate and indicate in the contract that the steel pipe can be galvanized for delivery. When the steel pipe is delivered by galvanizing, the relevant requirements for the galvanized layer shall comply with the provisions of Appendix A.
6 Test methods
6.1 The chemical analysis of the steel pipe is sampled according to the rules of GB/T 2006 6 . Chemical composition analysis is usually carried out according to GB/T 4336, GB/T 20123, GB/T 201 24, GB/T 20125 or other common methods. The arbitration shall be in accordance with GB/T 223. 5, GB/T 223. GB/T 223. 11. GB/T 223. 12. GB/T 223. 14. GB/T 223. 19. GB/T 223. 23. GB/T 223. 26. GB/T 223.37, GB/T 223. 40. GB/T 223. 60. GB/T 223. 62. GB/T 223. 63. GB/T 223. 68. GB/T 223.78, GB/T 223. 84 , GB/T 223. 86, GB/T 20125 provisions.
6.2 The size and shape of the steel pipe shall be measured with a gage that meets the accuracy requirements.
6.3 The inner and outer surfaces of steel pipes shall be visually inspected under adequate lighting conditions.
6.4 Sampling methods and test methods for other inspection items of steel pipes shall comply with the requirements of Table 11.
7 Inspection rules
7.1 Inspection and acceptance
The inspection and acceptance of steel pipes shall be carried out by the supplier's quality and technical supervision department.
7.2 Batch rule
7.2.2 Steel pipes are inspected and accepted in batches.
7 . 2 . 2 If the steel pipe is not heat treated after it has been cut into individual pieces, all pipe sections taken from a tube blank steel pipe shall be regarded as one.
7 . 2 . 3 Each batch shall consist of steel pipes of the same grade, the same heat number, the same specification and the same heat treatment system (heating). The quantity of each batch of steel pipes shall not exceed the following provisions:
a) The outer diameter is not more than 76 mm, and the wall thickness is not more than 3 mm: 400.
b) The outer diameter is greater than 351 mm: 50 roots.
c) Other sizes: 200 pieces.
d) The number of remaining steel pipes, if not less than 50% of the above-mentioned provisions, is separately listed as a batch, and less than 50% of the above-mentioned provisions can be incorporated into the same grade, the same furnace number and the same specification. In a batch.
7.3 Number of samples
The sampling quantity of each batch of steel pipe inspection shall comply with the provisions of Table 11.
7.4 Re-inspection and decision rules
The re-inspection and determination rules of steel pipes shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 21 02.
8 Packaging, sign and quality certificate
The packaging, marking and quality certificate of steel pipes shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 2102.
Seamless steel tubes for structural purposes
1 Scope
This standard specifies the order content, size, shape, weight, technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, packaging, and seamlessness of structural seamless steel tubes.
Sign and quality certificate.
This standard applies to seamless steel tubes for mechanical structures and general engineering structures.
2. Normative references
3. Ordering content
Contracts or orders for ordering steel pipes in accordance with this standard shall include the following:
a) standard number;
b) product name;
c) the grade of the steel, the quality grade should include the quality grade;
d) size specifications;
e) the quantity ordered (total weight or total length);
f) delivery status;
g) Special requirements.
4 size, shape and weight
4.1 outer diameter and wall thickness
The nominal outer diameter (D) and nominal wall thickness (S) of the steel pipe shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 1 7395. According to the requirements of the purchaser, other steel pipes of outer diameter and wall thickness can be supplied through negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
4.2 Allowable deviation of outer diameter and wall thickness
4.2.2 The allowable deviation of the outer diameter of the steel pipe shall comply with the requirements of Table 1.
Table 1 Allowable deviation of outer diameter of steel pipe in millimeters
| Steel pipe type | Allowable deviation |
| Hot rolled (expanded) steel pipe | ± 1% D or ±0. 5, whichever is the larger |
| Cold drawn (rolled) steel pipe | ± 0.75 %D or ±0. 3, whichever is the larger |
4.2.2 The allowable deviation of the wall thickness of the hot milk (expanded) steel pipe shall comply with the requirements of Table 2.
Table 2 Allowable deviation of wall thickness of hot rolled (expanded) steel pipe in millimeters
| Steel pipe type | Steel pipe nominal diameter D | S/D | Allowable deviation |
| Hot rolled steel pipe | ≤102 | — | ±1 2. 5% S or ±0. 4, whichever is the larger |
| >102 | ≤0.05 | ± 1 5 % S or ±0. 4, whichever is the larger | |
| >0. 05 〜0.10 | ±1 2. 5% S or ±0. 4, whichever is the larger | ||
| >0. 1 0 |
+ 12. 5%S - 1 0 % S |
||
| Cold drawn steel pipe | — | ± 1 5 % S |
4.2.3 The allowable deviation of the wall thickness of the cold drawn (milk) steel pipe shall comply with the requirements of Table 3.
Table 3 Allowable deviation of cold-drawn (milk) steel pipe wall thickness in millimeters
| Type of Steel pipe | Steel pipe nominal wall thickness S | Allowable deviation |
| Cold drawn steel pipe | ≤3 | (+1 5 % S,- 1 0 % s) Or ±0. 1 5, whichever is the larger |
| > 3 〜 10 |
+ 12. 5% S - 1 0 %S |
|
| > 1 0 | ± 1 0 %S |
4 . 2 . 4 According to the requirements of the purchaser, after consultation between the supplier and the buyer, and in the contract, the steel pipe with the allowable deviation of the dimensions specified in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 may be supplied.
4 . 3 length
4 . 3 . 1 normal length
The normal length of steel pipes is 3 000 mm to 12 000 mm. According to the requirements of the purchaser, steel pipes outside the normal length can be supplied through negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
4 . 3 . 2 range length
According to the requirements of the purchaser, after consultation between the supplier and the buyer, and in the contract, the steel pipe can be delivered according to the length of the scope.
4 . 3 . 3 length and length
4. 3. 3. 1 According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supplier and the buyer shall negotiate and indicate in the contract that the steel pipe can be delivered according to the length of the fixed length or the length of the double.
4. 3. 3. 2 When the steel pipe is delivered in fixed length or multiple length, the length tolerance shall comply with the following requirements:
a) When the length of the fixed length or the length of the double length is not more than 6 000 m, the allowable deviation is (+30,0) mm;
b) When the length of the ruler or the length of the ruler is greater than 6 000 m, the allowable deviation is (+50,0) mm.
4. 3. 3. 3 When the steel pipe is delivered in multiple lengths, the length of each double length shall be set as follows:
a) When D≤159 mm, the remaining amount of the incision is 5 mm~10 mm;
b) When D >159 mm, the remaining allowance is 10 mm~15 mm.
Steel pipes of other incisions can be supplied through negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
4 . 4 bending
4.4.1 The bending per meter of steel pipe shall comply with the requirements of Table 4.
Table 4 Bending degree of steel pipe
| Steel pipe nominal wall thickness S/mm | Bend per meter / (mm / m) |
| ≤1 5 | ≤1.5 |
| > 1 5 〜 30 | ≤2.0 |
| > 3 0 or D ≥351 | ≤3.0 |
4.4.2 The full-length bending of the steel pipe shall not exceed 0.15% of the total length of the steel pipe.
4. 5 Unroundness and uneven wall thickness
According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supplier and the buyer shall negotiate and indicate in the contract that the out-of-roundness and wall thickness of the steel pipe shall not exceed 80% of the nominal outer diameter tolerance and the nominal wall thickness tolerance respectively.
4 . 6 end shape
4.6.1 The steel pipe with a nominal outer diameter of not more than 60mm shall have a pipe end notching of more than 1.5 mm; for a steel pipe with a nominal outer diameter of more than 60 mm, the pipe end inclination shall not exceed 2.5% of the nominal outer diameter of the steel pipe, but the maximum shall be No more than 6 mm. The skew of the steel pipe is shown in Figure 1.

4 . 6 . 2 End cuts of steel pipes The burrs should be removed.
4 . 7 weight
4.7.1 The steel pipe is delivered according to the actual weight and can also be delivered according to the theoretical weight. The theoretical weight of the steel tube is calculated according to the provisions of GB/T 17395, and the density of the steel is 7.85 kg/dm3.
4 . 7 . 2 According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supplier and the buyer shall negotiate and indicate in the contract that the deviation between the theoretical weight of the delivered steel pipe and the actual weight shall comply with the following provisions:
a) Single steel pipe: ±10%;
b) Steel pipes with a minimum of 10 t per batch: ± 7.5 %.
5 Technical requirements
5. 1 Steel grade and chemical composition
5.1.1 The grade and chemical composition of the high-quality carbon structural steel (melting analysis) shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 699.
5.1.2 The grade and chemical composition of the low-alloy high-strength structural steel (melting analysis) shall comply with the requirements of Table 5. Except for quality class A, the carbon equivalent of each grade shall comply with the requirements of Table 6. The carbon equivalent (CEV) should be calculated from the smelting analysis component according to formula (1).
CEV = C + Mn/6 + (Cr + Mo + V) /5 + (Ni + Cu) /15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .(1)
5.1.3 Alloy structural steel grades and chemical composition (melting analysis) shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 3077.
5. 1. 4 According to the requirements of the purchaser, steel pipes of other grades or chemical compositions may be supplied through negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
5 . 1 . 5 When the purchaser requests to perform a finished product analysis, it should be indicated in the contract. The allowable deviation of the chemical composition of the finished steel pipe shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 222.
Table 5 Grades and chemical compositions of low-alloy high-strength structural steel
| Grade | Quality level | Chemical composition (mass fraction) % | ||||||||||||||
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Nb | V | Ti | Cr | Ni | Cu | N d | Mo | B | Alse | ||
| ≤ | ≥ | |||||||||||||||
| Q345 | A | 0.20 | 0.50 | 1.70 | 0.035 | 0.035 | - | - | - | 0.30 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 0.012 | 0.10 | — | — |
| B | 0.035 | 0.035 | ||||||||||||||
| C | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.015 | ||||||||||
| D | 0.18 | 0.030 | 0.025 | |||||||||||||
| E | 0.025 | 0.020 | ||||||||||||||
| Q390 | A | 0.20 | 0.50 | 1.70 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 0.015 | 0.10 | — | — |
| B | 0.035 | 0.035 | ||||||||||||||
| C | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.015 | |||||||||||||
| D | 0.030 | 0.025 | ||||||||||||||
| E | 0.025 | 0.020 | ||||||||||||||
| Q420 | A | 0.20 | 0.50 | 1.70 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.80 | 0.20 | 0.015 | 0.20 | — | — |
| B | 0.035 | 0.035 | ||||||||||||||
| C | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.015 | |||||||||||||
| D | 0.030 | 0.025 | ||||||||||||||
| E | 0.025 | 0.020 | ||||||||||||||
| Q460 | C | 0.20 | 0.60 | 1.80 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.80 | 0.20 | 0.015 | 0.20 | 0.005 | 0.015 |
| D | 0.030 | 0.025 | ||||||||||||||
| E | 0.025 | 0.020 | ||||||||||||||
| Q500 | C | 0.18 | 0.60 | 1.80 | 0.025 | 0.020 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 0.20 | 0.015 | 0.20 | 0.005 | 0.015 |
| D | 0.025 | 0.015 | ||||||||||||||
| E | 0.020 | 0.010 | ||||||||||||||
| Q550 | C | 0.18 | 0.60 | 2.00 | 0.025 | 0.020 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.20 | 0.015 | 0.30 | 0.005 | 0.015 |
| D | 0.025 | 0.015 | ||||||||||||||
| E | 0.020 | 0.010 | ||||||||||||||
| Q620 | C | 0.18 | 0.60 | 2.00 | 0.025 | 0.020 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.20 | 0.015 | 0.30 | 0.005 | 0.015 |
| D | 0.025 | 0.015 | ||||||||||||||
| E | 0.020 | 0.010 | ||||||||||||||
| Q690 | C | 0.18 | 0.60 | 2.00 | 0.025 | 0.020 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.20 | 0.015 | 0.30 | 0.005 | 0.015 |
| D | 0.025 | 0.015 | ||||||||||||||
| E | 0.020 | 0.010 | ||||||||||||||
|
a In addition to the Q345A and Q345B grades, the steel should contain at least one of the refined crystal elements Al, Nb, V, and T i . The supplier may add one or more of the refined crystal elements as needed, and the maximum value shall comply with the requirements in the table. When combined, Nb+ V + Ti< 0 . 2 2 %. b For Q345, Q390, Q420 and Q460 grades, M〇+ Cr< 0 . 3 0 %. c When Cr and N i of each grade are used as residual elements, the content of Cr and Ni should be no more than 0.30%; when it is required to be added, the content should meet the requirements in the table or be determined by the supplier and the buyer. d The supplier can ensure that the nitrogen content meets the requirements in the table, and the nitrogen content analysis is not performed. If alloying elements such as Al, Nb, V, and T i with nitrogen fixation are added to the steel, the nitrogen content is not limited, and the nitrogen content of the nitrogen should be indicated in the quality certificate. e When all aluminum is used, the total aluminum content is Alt > 0. 0 2 0 %. |
||||||||||||||||
Table 6 Carbon equivalent
| Grade | Carbon quantity CEV (mass fraction) / % | |||||
| Nominal wall thickness S < 16 mm | Nominal wall thickness S > 16 mm ~ 30 mm | Nominal wall thickness S > 3 0 mm | ||||
| Hot rolled or normalized | Quenching + tempering | Hot rolled or normalized | Quenching + tempering | Hot rolled or normalized | Quenching + tempering | |
| Q 345 | ≤0. 45 | — | ≤0.47 | — | ≤0.48 | — |
| Q 390 | ≤0. 46 | — | ≤0.48 | — | ≤0.49 | — |
| Q 420 | ≤0.48 | — | ≤0.50 | ≤0.48 | ≤0.52 | ≤0.48 |
| Q 460 | ≤0.53 | ≤0.48 | ≤0.55 | ≤0.50 | ≤0.55 | ≤0.50 |
| Q 500 | — | ≤0.48 | — | ≤0.50 | — | ≤0.50 |
| Q 550 | — | ≤0.48 | — | ≤0.50 | — | ≤0.50 |
| Q 620 | — | ≤0.50 | — | ≤0.52 | — | ≤0.52 |
| Q 690 | — | ≤0.50 | — | ≤0.52 | — | ≤0.52 |
5 . 2 Manufacturing methods
5 . 2 . 1 steel smelting method
Steel should be smelted by electric arc furnace plus furnace refining or oxygen converter plus furnace refining method. After consultation between the supply and demand sides, other methods of higher requirements may also be used for smelting. When the purchaser specifies a certain smelting method, it should be indicated in the contract.
Manufacturing Method 5. 2.2 shell of
5. 2. 2. 1 Tube blanks can be manufactured by continuous casting, die casting or hot milk (forging).
5. 2. 2. 2 continuous casting tube blanks shall comply with the provisions of YB/T 4149; hot milk (forged) tube blanks shall comply with the provisions of YB/T 5221 or YB/T 5222; the molded tube blanks may refer to hot milk ( The implementation of the forging) tube blank.
5 . 2 . 3 manufacturing method of steel pipe
Steel pipes shall be manufactured by hot milk (expansion) or cold drawing (milk) without seaming. When the purchaser specifies a method to manufacture steel pipes, it should be indicated in the contract.
5 . 3 delivery status
5.3.1 Hot milk (expanded) steel pipes are delivered in hot milk (expanded) or heat treated condition. When the purchaser requests the heat treatment status, it shall be indicated in the contract.
5 . 3 . 2 Cold drawn (milk) steel pipes shall be delivered in an annealed or high temperature tempered condition. According to the requirements of the purchaser, after consultation between the supplier and the buyer, and in the contract, the cold drawn (milk) steel pipe can also be delivered in cold drawn (milk) or other heat treatment conditions.
5.4 Mechanical properties
5 . 4 . 1 tensile properties
5.4.1.1 For steel pipes of high quality carbon structural steel and low alloy high strength structural steel, the tensile properties in the delivery state shall comply with the requirements of Table 7.
5. 4. 1. 2 alloy structural steel pipe specimen blanks According to the recommended heat treatment system in Table 8, the tensile properties measured after the heat treatment is prepared shall comply with the requirements of Table 8.
5. 4. 1. 3 Cold drawing (milk) state The mechanical properties of the delivered steel pipe shall be determined by negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
GB/T 8162—2018
Table 7 Mechanical properties of high quality carbon structural steel and low alloy high strength structural steel pipe
| Grade | quality level |
Tensile strength Rm/M Pa |
Lower yield strength MPa Nominal wall thickness S |
Elongation | Impact test | |||
| ≤1 6 mm |
>16 mm 〜 30 mm |
〉 30 mm | Temperature | Absorb energy | ||||
| ≥ | ≥ | |||||||
| 10 | — | ≥335 | 205 | 195 | 185 | 24 | — | — |
| 15 | — | ≥375 | 225 | 215 | 205 | 22 | — | — |
| 20 | — | ≥410 | 245 | 235 | 225 | 20 | — | — |
| 25 | — | ≥450 | 275 | 265 | 255 | 18 | — | — |
| 35 | — | ≥510 | 305 | 295 | 285 | 17 | — | — |
| 45 | — | ≥590 | 335 | 325 | 315 | 14 | — | — |
| 20 Mn | — | ≥450 | 275 | 265 | 255 | 20 | — | — |
| 25 Mn | — | ≥490 | 295 | 285 | 275 | 18 | — | — |
| Q 345 | A | 470〜 630 | 345 | 325 | 295 | 20 | — | — |
| B | + 20 | 34 | ||||||
| C | 21 | 0 | ||||||
| D | - 20 | |||||||
| E | - 40 | 27 | ||||||
| Q 390 | A | 490〜 650 | 390 | 370 | 350 | 18 | — | — |
| B | + 20 | 34 | ||||||
| C | 19 | 0 | ||||||
| D | - 20 | |||||||
| E | - 40 | 27 | ||||||
| Q 420 | A | 520〜 680 | 420 | 400 | 380 | 18 | — | — |
| B | + 20 | 34 | ||||||
| C | 19 | 0 | ||||||
| D | - 20 | |||||||
| E | - 40 | 27 | ||||||
| Q 460 | C | 550〜 720 | 460 | 440 | 420 | 17 | 0 | 34 |
| D | - 20 | |||||||
| E | - 40 | 27 | ||||||
| Q 500 | C | 610〜 770 | 500 | 480 | 440 | 17 | 0 | 55 |
| D | - 20 | 47 | ||||||
| E | - 40 | 31 | ||||||
| Q 550 | C | 670〜 830 | 550 | 530 | 490 | 16 | 0 | 55 |
| D | - 20 | 47 | ||||||
| E | - 40 | 31 | ||||||
| Q 620 | C | 710〜 880 | 620 | 590 | 550 | 15 | 0 | 55 |
| D | - 20 | 47 | ||||||
| E | - 40 | 31 | ||||||
| Q 690 | C | 770〜 940 | 690 | 590 | 620 | 14 | 0 | 55 |
| D | - 20 | 47 | ||||||
| E | - 40 | 31 | ||||||
Table 8 Mechanical properties of alloy steel pipes
| Grade | Heat treatment a | Tensile properties b |
Brinell hardness HBW |
||||||
| Quenching (normalizing) | Temper | Tensile strength MPa | Lower yield strength MPa | Elongation % | |||||
| Temperature °C | Coolant | Temperature °C | Coolant | ||||||
| The first time | The second time | ≥ | ≤ | ||||||
| 40Mn2 | 840 | — | Water, oil | 540 | Water, oil | 885 | 735 | 12 | 217 |
| 45Mn2 | 840 | — | Water, oil | 550 | Water, oil | 885 | 735 | 10 | 217 |
| 27SiMn | 920 | — | Water | 450 | Water, oil | 980 | 835 | 12 | 217 |
| 40MnB | 850 | — | oil | 500 | Water, oil | 980 | 785 | 10 | 207 |
| 45MnB | 840 | — | oil | 500 | Water, oil | 1 030 | 835 | 9 | 217 |
| 20Mn2B | 880 | — | oil | 200 | Water, air | 980 | 785 | 10 | 187 |
| 20Cr | 880 | 800 | Water, oil | 200 | Water, air | 835 |
540 490 |
10 10 |
179 179 |
| 30Cr | 860 | — | oil | 500 | Water, oil |
785 885 |
685 | 11 | 187 |
| 35Cr | 860 | — | oil | 500 | Water, oil | 930 | 735 | 11 | 207 |
| 40Cr | 850 | — | oil | 520 | Water, oil | 980 | 785 | 9 | 207 |
| 45Cr | 840 | — | oil | 520 | Water, oil | 1 030 | 835 | 9 | 217 |
| 50Cr | 830 | — | oil | 520 | Water, oil | 1 080 | 930 | 9 | 229 |
| 38CrSi | 900 | — | oil | 600 | Water, oil | 980 | 835 | 12 | 255 |
| 20CrMo | 880 | — | Water, oil | 500 | Water, oil |
885 845 |
685 635 |
11 12 |
197 197 |
| 35CrMo | 850 | — | oil | 550 | Water, oil | 980 | 835 | 12 | 229 |
| 42CrMo | 850 | — | oil | 560 | Water, oil | 1 080 | 930 | 12 | 217 |
| 38CrMoAl | 940 | — | Water, oil | 640 | Water, oil |
980 930 |
835 785 |
12 14 |
229 229 |
| 50CrVA | 860 | — | oil | 500 | Water, oil | 1 275 | 1 130 | 10 | 255 |
| 20CrMn | 850 | — | oil | 200 | Water, air | 930 | 735 | 10 | 187 |
| 20CrMnSi | 880 | — | oil | 480 | Water, oil | 785 | 635 | 12 | 207 |
| 30CrMnSi | 880 | — | oil | 520 | Water, oil |
1 080 980 |
635 835 |
8 10 |
229 229 |
| 35CrMnSiA | 880 | 870 | oil | 230 | Water, oil | 1 620 | — | 9 | 229 |
| 20CrMnTi | 880 | 850 | oil | 200 | Water, oil | 1 080 | 835 | 10 | 217 |
| 30CrMnTi | 880 | 780 | oil | 200 | Water, oil | 1 470 | — | 9 | 229 |
| 12CrNi2 | 860 | 780 | Water, oil | 200 | Water, oil | 785 | 590 | 12 | 207 |
| 12CrNi3 | 860 | 780 | oil | 200 | Water, oil | 930 | 685 | 11 | 217 |
| 12Cr2Ni4 | 860 | oil | 200 | Water, oil | 1 080 | 835 | 10 | 269 | |
| 40CrNiMoA | 850 | — | oil | 600 | Water, oil | 980 | 835 | 12 | 269 |
| 45CrNiMoVA | 860 | — | oil | 400 | oil | 1 470 | 1 325 | 7 | 269 |
5 . 4. 2 hardness
Alloy structure steel pipes with annealed or high temperature tempered condition and wall thickness not less than 5 m m shall have a Brinell hardness as specified in Table 8.
5.4.3 Impact
5. 4. 3. 1 Low-alloy high-strength structural steel pipe, when the outer diameter is not less than 70 mm and the wall thickness is not less than 6.5 mm, the longitudinal impact test shall be carried out, and the test temperature of the Charpy V-notch impact test and The energy absorbed by the impact shall comply with the requirements of Table 7. The shock absorption energy is calculated as the arithmetic mean of a set of 3 samples, allowing a single value of one of the samples to be lower than the specified value, but not less than 70% of the specified value.
5. 4. 3. 2 The impact absorption energy in Table 7 is the Charpy V-notch impact absorption energy requirement value of the standard size sample. When the size of the steel pipe cannot prepare a standard size sample, a small size sample can be prepared. When using small-sized impact specimens, the minimum Charpy V-notch impact energy requirements should be the standard-size specimen impact energy requirements multiplied by the decreasing factor in Table 9. The size of the impact specimen should be preferentially selected to a larger size.
Table 9 Impact absorption power reduction coefficient of small size samples
| Specimen specification | Sample size (height X width) / mm | Decreasing coefficient |
| Standard size | 1 0 X 10 | 1.00 |
| Small sample | 1 0 X 7.5 | 0.75 |
| Small sample | 1 0 X 5 | 0.50 |
5. 4. 3. 3 According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supplier and the buyer shall negotiate and indicate in the contract that the other grades of the steel pipe may also be subjected to the Charpy V-notch impact test. The test temperature, test size and impact absorption energy are The supply and demand sides will negotiate and determine.
5 . 5 process performance
5 . 5 . 1 flattening
The grades are 10, 15, 20, 25, 20Mn, 25Mn, Q345, Q390, the nominal outer diameter is >22 mm~600mm, and the steel pipe with the wall thickness to outer diameter ratio of not more than 10% shall be crushed and tested. The distance between the plates should meet the requirements of Table 10. After crushing, on the sample
There should be no cracks or cracks.
Table 10 Distance between flat steel plates
| Grade | Flattening test flat board spacing Ha/mm |
| 1 0、1 5、20、25 | D X 2/3 |
| Q 345. Q 390. 20 Mn . 25 Mn | D X 7/8 |
| The minimum plate spacing (H) for the flattening test shall be 5 times the wall thickness of the steel tube. | |
5.5.2 Bending
According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supply and demand sides negotiate and indicate in the contract that the steel pipe with an outer diameter of not more than 22mm can be bent. The bending angle is 90°, and the radius of the core is 6 times the outer diameter of the steel pipe. There should be no cracks or cracks in the bend.
5 . 6 surface quality
The inner and outer surfaces of the steel pipe should not have visible cracks, folds, crusting, milk breaks and separation. These defects shall be completely removed and the depth of removal shall not exceed the lower deviation of the nominal wall thickness. The actual wall thickness at the cleaning site shall not be less than the minimum allowed by the wall thickness. Other local imperfections that do not exceed the deviation below the wall thickness are allowed to exist.
5 . 7 Nondestructive testing
According to the requirements of the purchaser, after consultation between the supplier and the buyer, and in the contract, the steel pipe can be non-destructively tested by one or more of the following methods:
A) The ultrasonic testing predetermined GB / T 5777-2008, and comparison sample tube groove depth levels: cold drawing (rolled) pipe for L3, rolled (expanded) steel pipe L4;
b) eddy current inspection according to the provisions of GB/T 7735—201 6 , acceptance level E4H or E4;
c) Magnetic flux leakage test according to GB/T 12606—201 6 and acceptance level F4.
5 . 8 galvanized layer
According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supply and demand sides negotiate and indicate in the contract that the steel pipe can be galvanized for delivery. When the steel pipe is delivered by galvanizing, the relevant requirements for the galvanized layer shall comply with the provisions of Appendix A.
6 Test methods
6.1 The chemical analysis of the steel pipe is sampled according to the rules of GB/T 2006 6 . Chemical composition analysis is usually carried out according to GB/T 4336, GB/T 20123, GB/T 201 24, GB/T 20125 or other common methods. The arbitration shall be in accordance with GB/T 223. 5, GB/T 223. GB/T 223. 11. GB/T 223. 12. GB/T 223. 14. GB/T 223. 19. GB/T 223. 23. GB/T 223. 26. GB/T 223.37, GB/T 223. 40. GB/T 223. 60. GB/T 223. 62. GB/T 223. 63. GB/T 223. 68. GB/T 223.78, GB/T 223. 84 , GB/T 223. 86, GB/T 20125 provisions.
6.2 The size and shape of the steel pipe shall be measured with a gage that meets the accuracy requirements.
6.3 The inner and outer surfaces of steel pipes shall be visually inspected under adequate lighting conditions.
6.4 Sampling methods and test methods for other inspection items of steel pipes shall comply with the requirements of Table 11.
Table 11 Inspection items of steel pipes, sampling quantity, sampling method, test method
| Test items | Number of samples | Sampling method | Detection method |
| Chemical composition | Take 1 sample per furnace | GB/T 20066 | |
| Stretching test | Take 1 sample on each of two steel tubes in each batch | GB/T 2975 | GB/T 228.1 |
| Hardness test | Take 1 sample on each of two steel tubes in each batch | GB/T 231.1 | GB/T 231.1 |
| Impact test | Take one set of 3 samples on each of the two steel pipes in each batch | GB/T 2975 | GB/T 229 |
| Flattening test | Take 1 sample on each of two steel tubes in each batch | GB/T 246 | GB/T 246 |
| Bending test | Take 1 sample on each of two steel tubes in each batch | GB/T 244 | GB/T 244 |
| Ultrasonic testing | Root by root | — | GB/T 5777— 2008 |
| Eddy current testing | Root by root | — | GB/T 7735— 2016 |
| Leak detection | Root by root | — | GB/T 12606— 2016 |
| Galvanized layer | |||
7 Inspection rules
7.1 Inspection and acceptance
The inspection and acceptance of steel pipes shall be carried out by the supplier's quality and technical supervision department.
7.2 Batch rule
7.2.2 Steel pipes are inspected and accepted in batches.
7 . 2 . 2 If the steel pipe is not heat treated after it has been cut into individual pieces, all pipe sections taken from a tube blank steel pipe shall be regarded as one.
7 . 2 . 3 Each batch shall consist of steel pipes of the same grade, the same heat number, the same specification and the same heat treatment system (heating). The quantity of each batch of steel pipes shall not exceed the following provisions:
a) The outer diameter is not more than 76 mm, and the wall thickness is not more than 3 mm: 400.
b) The outer diameter is greater than 351 mm: 50 roots.
c) Other sizes: 200 pieces.
d) The number of remaining steel pipes, if not less than 50% of the above-mentioned provisions, is separately listed as a batch, and less than 50% of the above-mentioned provisions can be incorporated into the same grade, the same furnace number and the same specification. In a batch.
7.3 Number of samples
The sampling quantity of each batch of steel pipe inspection shall comply with the provisions of Table 11.
7.4 Re-inspection and decision rules
The re-inspection and determination rules of steel pipes shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 21 02.
8 Packaging, sign and quality certificate
The packaging, marking and quality certificate of steel pipes shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 2102.
