GB 24512 Part 2 Alloy Steel Seamless Tubes And Pipes
GB 24512 Part 2 Alloy steel seamless tubes and pipes
GB 24512 . 1—2009 Seamless steel tubes and pipes for nuclear power plants - Part 2: Alloy steel seamless tubes and pipes
GB 24512 . 1—2009 Seamless steel tubes and pipes for nuclear power plants - Part 2: Alloy steel seamless tubes and pipes
Scope
This part of GB 24512 specifies the classification, code, size, shape, weight and tolerance, technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, packaging, marking and quality reports of alloy steel seamless steel tubes for nuclear power plants.
This section applies to the manufacture of alloy steel seamless steel tubes for pressure-bearing parts of nuclear power plants.
Classification and code
The seamless steel pipes in this section are divided into two categories according to the manufacturing method of the products. The categories and codes are as follows:
a) hot-rolled (extruded, top, forged, expanded) steel pipe, codenamed W-H;
b) Cold drawn (rolled) steel pipe, codenamed W-C.
The seamless steel pipes in this section are divided into two categories according to their dimensional accuracy. The categories and codes are as follows:
a) General level accuracy, codenamed PA;
b) Advanced precision, codenamed PC.
The following codes are applicable to this section:
D outer diameter (if the nominal outer diameter or the outer diameter is not specified, it is the nominal outer diameter or the calculated outer diameter)
S wall thickness (if the nominal wall thickness or minimum wall thickness is not specified, it is the nominal wall thickness or the minimum wall thickness)
Smin minimum wall thickness
d nominal inner diameter
The grade of 4 steel consists of the first capital letter (HD) and chemical composition of Chinese Pinyin, which represents the use of nuclear power.
For example: HD15NiMnMoNbCu
among them:
HD one "one nuclear power" Chinese pinyin first capital letter;
15NiMnMoNbCu -15 represents the average carbon content, followed by the specified alloying element symbols and the Arabic numerals representing the average content of the alloying elements.
According to the requirements of the purchaser, the steel pipe may be delivered according to the nominal outer diameter and minimum wall thickness, nominal inner diameter and nominal wall thickness or other dimensional specifications after negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
When the steel pipe is delivered in fixed length, the length tolerance shall comply with the following requirements:
When the steel pipe is delivered in the length of the double ruler, the length of each double ruler shall be set as follows: a) When D≤ 159 mm, the remaining allowance is 5mm~10mm;
For steel pipes with D ≥ 127 mm, the full-length bending should be no more than 0.10% of the total length of the steel pipe.
Calculation of theoretical weight
Weight tolerance
Tube blank manufacturing methods and requirements
Outer diameter and wall thickness
Steel pipes shall be delivered according to the nominal outer diameter and nominal wall thickness. The nominal outer diameter and nominal wall thickness of the steel pipe shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 17395.
According to the requirements of the purchaser, the steel pipe may be delivered according to the nominal outer diameter and minimum wall thickness, nominal inner diameter and nominal wall thickness or other dimensional specifications after negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
According to the requirements of the purchaser, steel pipes of different sizes than those specified in GB / T 17395 can be supplied through negotiation between the supplier and the buyer.
Note: If the nominal wall thickness or minimum wall thickness is not specified. The “wall thickness” described in this section is the nominal wall thickness or the minimum wall thickness; if the nominal outer diameter or the calculated outer diameter is not specified, the “outer diameter” in this section is the nominal outer diameter or the calculated outer diameter.
Allowable deviation of outer diameter and wall thickness
When the steel pipe is delivered according to the nominal outer diameter and the nominal wall thickness, the allowable deviation of the nominal outer diameter and the nominal wall thickness shall comply with the requirements of Table 1.
When the steel pipe is delivered according to the nominal outer diameter and the minimum wall thickness, the allowable deviation of the nominal outer diameter shall comply with the provisions of Table 1. The allowable deviation of the wall thickness shall comply with the requirements of Table 2.
When the steel pipe is delivered according to the nominal inner diameter and the nominal wall thickness, the allowable deviation of the nominal inner diameter is ± 1 % d. The allowable deviation of the nominal wall thickness shall comply with the requirements of Table 1.
When the demander does not specify the allowable deviation level of the manifold size in the contract. The allowable deviation of the outer diameter and wall thickness of the steel pipe shall comply with the general grade.
According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supplier and the buyer shall negotiate and indicate in the contract that the steel pipe with the allowable deviation of the dimensions specified in Tables 1 and 2 or other steel pipes with the allowable deviation of the inner diameter may be supplied.
Table 1 Allowable deviation of nominal outer diameter and nominal thickness of steel pipe
| Classification | Manufacturing method | Size | Allowable deviation | ||
| PA | PC | ||||
| W-H | Hot rolled steel pipe | D | ≤54 | ±0.40 | ±0.30 |
| >54 | ±1%D | ±0.75%D | |||
| S | ≤4.0 | ±0.45 | ±0.35 | ||
| >4.0-20 |
+12.5%S -10%S |
±10%S | |||
| >20,D<219 | ±10%S | ±7.5%S | |||
| >20,D≥219 |
+12.5%S -10%S |
±10%S | |||
| W-H | Thermal expansion steel pipe | D | All | ±1%D | ±0.75%D |
| S | All |
+18%S -10%S |
+12.5%S -10%S |
||
| W-C | Cold drawn steel pipe | D | ≤25.4 | ±0.15 | - |
| >25.4-40 | ±0.20 | - | |||
| >40-50 | ±0.25 | - | |||
| >50-60 | ±0.30 | - | |||
| >60 | ±0.5%D | - | |||
| S | ≤3.0 | ±0.3 | ±0.2 | ||
| >3.0 | ±10%S | ±7.5%S | |||
Table 2 Minimum wall thickness tolerance
| Classification | Manufacturing method | Wall thickness range | Allowable deviation | |
| PA | PC | |||
| W-H | Hot rolled steel pipe | Smin≤4.0 |
+0.9 0 |
+0.7 0 |
| Smin>4.0 |
+25%Smin 0 |
+22%Smin 0 |
||
| W-C | Cold drawn steel pipe | Smin≤3.0 |
+0.6 0 |
+0.4 0 |
| Smin>3.0 |
+20%Smin 0 |
+15%Smin 0 |
||
Usual length
The normal length of steel pipes is 4000 mm to 12000 mm.
After consultation between the supplier and the purchaser, and in the contract, it is possible to deliver steel pipes with a length greater than 1 000 mm or shorter than 4000 mm but not shorter than 300 mm. Steel pipes with a length shorter than 4000 mm but not shorter than 3000 mm shall not exceed 5% of the total delivered quantity of the steel pipe.
Length and length
According to the requirements of the purchaser, after consultation between the supplier and the buyer, and in the contract, the steel pipe can be delivered according to the length of the fixed length or the length of the double.
When the steel pipe is delivered in fixed length, the length tolerance shall comply with the following requirements:
a) When D≤ 406.4 mm, +15mm;
b) D > 406.4 mm, + 20mm
When the steel pipe is delivered in the length of the double ruler, the length of each double ruler shall be set as follows: a) When D≤ 159 mm, the remaining allowance is 5mm~10mm;
b) 139 < D ≤ 406 .4mm, the remaining amount of the incision is 10mm ~ 15 mn,;
c) When D > 406.4 mm, the residual allowance is 10mm~20mm.
Bending
The bending per meter of steel pipe shall comply with the following requirements:
a) When S ≤ 15mm, it is not more than 1.5 mm / m.
b) When 15mm < S ≤ 30 mm, it is not more than 2.0 mm / m;
c) When S > 30 mm, it is not more than 3.0 mm/m.
For steel pipes with D ≥ 127 mm, the full-length bending should be no more than 0.10% of the total length of the steel pipe.
Unroundness and uneven wall thickness
According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supplier and the buyer will negotiate and indicate in the contract. The non-roundness and wall thickness of the steel pipe shall not exceed 80% of the outer diameter and wall thickness tolerance respectively.
end shape
The end faces of the steel pipe should be perpendicular to the axis of the steel pipe, and the incision burrs should be removed.
Delivery weight
Steel pipes are delivered according to the nominal outside diameter and nominal wall thickness or nominal inner diameter and nominal wall thickness. The steel pipe is delivered according to the actual weight and can also be delivered according to the theoretical weight.
When the steel pipe is delivered according to the nominal outer diameter and the minimum wall thickness, the steel pipe is delivered according to the actual weight; the supply and demand sides negotiate and the contract indicates that the steel pipe can also be delivered according to the theoretical weight.
Calculation of theoretical weight
The theoretical weight of the steel pipe is calculated according to the provisions of GB / T 17395 (the density of steel is 7. 85kg / dm3, ).
The steel pipe shall be delivered according to the nominal inner diameter and the nominal wall thickness. The theoretical weight shall be calculated by calculating the outer diameter. The calculated outer diameter is the outer diameter value calculated according to the nominal inner diameter and the nominal wall thickness; the steel pipe shall be delivered according to the minimum wall thickness. The wall thickness calculates the theoretical weight, and the average wall thickness is the average of the maximum and minimum wall thicknesses calculated from the wall thickness and its allowable deviation.
Weight tolerance
According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supplier and the buyer shall negotiate and indicate in the contract that the deviation between the actual weight of the delivered steel pipe and the theoretical weight shall comply with the following provisions:
b) Single steel pipe: ±10%.
b) Steel pipe with a minimum of 10t per batch: ±7.5%.
Technical requirements
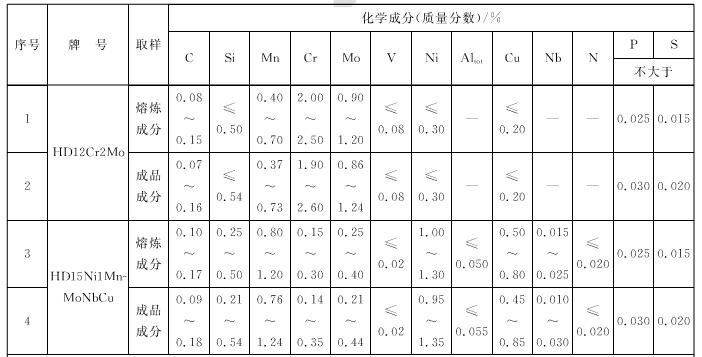
Steel grades and chemical composition
The grade and chemical composition (smelting and finished components) of the steel shall comply with the requirements of Table 3. The terms, definitions and determination methods for the chemical composition of the finished product shall be in accordance with GS /T 222.
Table 3 Steel grades and chemical composition

Manufacturing methods
Manufacturing Outline
Before the manufacture of steel pipes, the manufacturer shall establish a manufacturing outline, which shall include the various manufacturing and inspection processes in the manufacturing process.
Steel smelting method
Steel shall be refined by electric arc furnace plus refining and vacuum refining treatment, or refined by oxygen converter and refining by vacuum refining, or electroslag remelting. When the purchaser specifies a certain smelting method, it should be indicated in the contract
After consultation between the supplier and the purchaser, and indicating in the contract, other higher-required smelting methods may be adopted.
Tube blank manufacturing methods and requirements
Tube failure shall be made by continuous casting, chess casting or hot rolling (forging).
Continuous casting tube blanks shall comply with the provisions of YB / T 4149, in which the level of cracks, intermediate cracks, subcutaneous cracks and subcutaneous air bubbles of low-order tissue defects shall not exceed 1, respectively.
Hot rolled (forged) tube blanks shall comply with the provisions of YB / T 5137.
The head and tail of the cast tube blank (steel ingot) should have sufficient removal to ensure the quality of the steel pipe.
Manufacturing method of steel pipe
The steel pipe shall be manufactured by hot rolling (squeezing, topping, forging, expanding) or cold drawing (rolling). The hot expanded steel pipe shall refer to a steel pipe with a larger diameter and a larger diameter of the billet steel pipe after being integrally heated and deformed.
The total elongation factor (forging ratio) in the deformation of the steel tube shall not be less than 3 . The manufacturer shall adopt an appropriate manufacturing process to ensure uniformity of processing deformation in different parts of the steel pipe.
Delivery status
The steel pipe shall be delivered in a heat treated condition. The heat treatment system for steel pipes shall comply with the requirements of Table 4.
Test items
Chemical composition
Room temperature tensile test
High temperature tensile test
Impact test
Hydraulic test
Eddy current testing
Magnetic flux leakage test
Flattening test
Bending test
Flaring test
Low magnification test
Non-metallic inclusions
Grain size
Microstructure
Decarburization layer
Penetration test
Magnetic particle inspection
Ultrasonic flaw detection
Layered defect ultrasonic testing
Table 4 Heat treatment of steel pipe
| Grade | Heat treatment c | Austenitizing | Tempering |
Holding time |
||
| Heating temperature ℃ | Cooling medium | Heating temperature ℃ | Cooling medium | |||
| HD 12Cr2Mo | Normalizing, Quenching |
Normalizing:900-960 Quenching:≥900 |
Air | 700-750 | Air |
The normalizing heat preservation time is calculated according to the wall thickness per 1mm not less than min, but less than 20min.
Tempering holding time is not less than 1h |
| HD15NiMnMoNbCu | Normalizing, Quenching |
Normalizing:900-980 Quenching:880-930 |
Air | 630-680 | Air | |
Mechanical properties
Tensile properties
Tensile properties at room temperature
The room temperature tensile properties of the steel pipes in the delivery state shall comply with the requirements of Table 5.
Table 5 Tensile properties of steel pipes at room temperature
| Grade | Tensile strength Mpa | Plastic extension strength Mpa | Elongation | |
| Portrait | Landscape | |||
| HD 12Cr2Mo | 450~600 | ≥280 | ≥22 | ≥20 |
| HD15NiMnMoNbCu | 620~780 | ≥440 | ≥19 | ≥17 |
High temperature tensile properties
The high temperature tensile properties of the steel pipe in the delivery state shall comply with the requirements of Table 6.
Table 6 High temperature tensile properties of steel pipes
| Grade | Temperature ℃ | Tensile strength Mpa | Plastic extension strength Mpa | Elongation |
| HD 12Cr2Mo | 350 | - | ≥185 | - |
| HD15NiMnMoNbCu | 200 | ≥520 | ≥402 | ≥35 |
| 300 | ≥520 | ≥382 | ≥35 | |
| 400 | ≥500 | ≥343 | ≥35 |
Tensile test specimen
For steel pipes with an outer diameter of less than 219 mm, the tensile test shall be taken along the longitudinal direction of the steel pipe.
For steel pipes with an outer diameter of not less than 219 mm, when the size of the steel pipe permits, the tensile test shall take a circular cross-section sample along the transverse direction of the steel pipe. When the steel pipe is not large enough to take a circular cross-section specimen in the transverse direction, the tensile test shall be taken along the longitudinal direction of the steel pipe. The transverse circular cross-section specimen shall be taken from the final flattened sample.
Hardness
Delivery state steel pipe should be tested for Brinell hardness
Test items
Chemical composition
Room temperature tensile test
High temperature tensile test
Impact test
Hydraulic test
Eddy current testing
Magnetic flux leakage test
Flattening test
Bending test
Flaring test
Low magnification test
Non-metallic inclusions
Grain size
Microstructure
Decarburization layer
Penetration test
Magnetic particle inspection
Ultrasonic flaw detection
Layered defect ultrasonic testing
Test methods
The size and shape of the steel pipe shall be measured one by one using gauges that meet the accuracy requirements.
The inner and outer surfaces of the steel pipe shall be visually inspected under full lighting conditions.
Sampling methods for mechanical and process performance testing shall comply with the following provisions:
a) The sample shall be taken from the sample loop intercepted at one end of the steel pipe in the delivery state. The sample shall be of sufficient size to intercept all the samples required for the test and re-inspection;
b) The finished steel pipe made of steel ingot shall be taken from the end of the manifold corresponding to the mouth end of the steel ingot.
c) the distance from the end of the sample to the end of the pipe shall not be less than the wall thickness of the steel pipe, but shall not exceed 40 mm;
d) For steel pipes with a wall thickness of not more than 30 mm, the axis of the test for mechanical properties shall be located at one-half of the wall thickness of the steel pipe, and the steel pipe with a wall thickness greater than 30 mm shall be in the vicinity of the inner wall of the steel pipe. Intercepted in one quarter.
For steel tubes of nuclear grade 2 main steam pipelines and main water supply pipelines or for nuclear grade 1, 2, and 3 steel pipes with an outer diameter greater than 450 mm and a wall thickness greater than 20 mm, the sampling method shall comply with the provisions of Appendix C.
Packaging, marking and quality reports
Before the steel pipe is packed, the inner and outer surfaces of the steel pipe shall be cleaned by using oil-free, dry and clean compressed air or other suitable methods. The pipe ends of the steel pipe shall be sealed with plastic caps, plastic cloth, sackcloth or other suitable methods and materials.
Other provisions for steel pipe packaging shall comply with the provisions of GB / T2102.
According to the requirements of the purchaser, the supplier and the buyer shall negotiate and indicate in the contract that the outer surface of the steel pipe may be coated with anti-rust grease or anti-rust paint.
The marking of steel pipes shall comply with the provisions of GB / T 2102.
Regardless of the condition of the steel pipe before delivery. The manufacturer shall establish the following corresponding quality report after each inspection and provide the report to the acquirer:
a) steel smelting method, steel chemical composition smelting analysis and finished product analysis report;
b) Report on the manufacturing method of the tube blank.
c) heat treatment records and analysis reports;
d) mechanical and process performance test report,
e) visual inspection report of surface quality;
f) non-destructive testing report;
g) hydraulic test report;
h) When using steel ingots to manufacture nuclear grade 1 and 2 steel pipes, the minimum cut-off ratio report of the steel ingot head and tail;
i) Inspection reports for other specified inspection items. The following should also be included in these reports;
― smelting furnace number and steel pipe batch number;
― manufacturer identification mark;
― Order number (contract number);
― If necessary, check the name of the agency,
― The results of various tests and retests, and the specified values against them.
